By Tom Mills, Founder & Managing Director of Two Oceans Strategy, London,


2022 NOVEMBER ADVERTORIAL REVIEW 111/11 32 Deep-sea Mining: Environmental And Social Considerations And Risks.
UK. latest uranium/vanadium district: advanced exploration: argentina 26 is it possible for the iron ore mining industry to go green? 44 10 established a new and commendable battery system safety standard Sandvik Needs To Be Applauded In Underground Mining
2 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022 BIG RESULTS SMALL TEAM Optiro is a resource consulting and advisory group. Our 5 core services are Geology, Mining Engineering, Corporate, Training and Software. In eleven years, our team has travelled the world providing expertise to improve, value, estimate and audit the world’s minerals. Pound for pound we think you’ll find no-one delivers greater value –and BIG results. +$15 BILLION DEALS/ VALUATIONS >780 MILLION oz Au RESOURCE AUDITS >64 MILLION oz Au RESOURCE ESTIMATES >3,000 CLIENTS +2,000 PEOPLE TRAINED 24 COMMODITIES 53 COUNTRIES >4,300 MILLION lb NICKEL >5,100 MILLION lb COPPER+5 IRON ORE BILLION TONNES www.optiro.com contact@optiro.com +61 8 9215 0000


www.skillings.net | 3 THE LEAD 10 Sandvik Needs To Be Applauded In Underground Mining: Established A New and Commendable Bat tery System Safety Standard MINING EQUIPMENT 37 Mineral Management Software Suite 41 Slam Exploration Mobilizing to Drill Gold Veins at Menneval MINING JOBS 20 Job Growth In Coal Counties: VTS Targets Confirmed 22 Shale drillers Strug gle for Workforce PROFILES IN MINING 32 Deep-sea Mining: Environmental And Social Considerations And Risks. By Tom Mills, Founder & Managing Director of Two Oceans Strategy, London, UK. RARE EARTH 18 NioCorp CEO: Do Not Count On China For Rare Earth Metals SPECIAL FOCUS 26 Latest Uranium/Vanadium district: Advanced exploration: Argentina 30 Lithium Mining in North America 38 Coal Companies Reck lessly Going Go! 42 Fogmaker south africa: Dominate ema 2022 show: With Smart, Efficient And Cost-Effective Fire-Suppression Practices 44 Is It Possible For The Iron Ore Mining Industry To Go Green? SURFACE MINING 21 Gold Mining Stocks Bull ish Mid October 22 John
Robins
Joins Gelum Resources as Advisor 24 Fossil Fuel Growth Vs. Clean Energy’s Progress 29 2022 Great Lakes Marine Hall of Fame Inductees STATISTICS 46 August 2022 crude steel production 47 Crude steel production UNDERGROUND MINING 25 SolGold & Cornerstone Merger Transaction 41 CGG Awarded Critical mineral exploration Study in Argentina
Florida 34284
(888) 444 7854

USA.
4.
& Billing: 350 W. Venice Ave.
Venice, FL 34284.
Ave.
Florida 34284.
(888)
7854
(888) 261-6014.

UNITED STATES $72 Monthly in US Funds $109 Monthly in US Funds 1st Class Mail OUTSIDE OF UNITED STATES $250 US Monthly for 7 - 21 day delivery $335 US Monthly for Air Mail Service SUBSCRIPTIONS SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW NEWS ROOM Digital Monthly Magazine SMR Americas Monday Global Skillings Wednesday Skillings Equipment Gear Friday All funds are monthly $4.95 USD per month publisher CHARLES PITTS chas.pitts@skillings.net managing editor SAKSHI SINGLA sakshi.singla@skillings.net editor-in-chief JOHN EDWARD john.edward@skillings.net creative director MO SHINE mo.shine@skillings.net contributing editors ROB RAMOS AALIYAH ZOLETA MARIE GABRIELLE media production STANISLAV PAVLISHIN media.team@cfxnetwork.com media administrator SALINI KRISHNAN salini.krishnan@cfxnetwork.com director of sales & marketing CHRISTINE MARIE advertising@skillings.net profiles in mining mining.profiles@skillings.net general contact information info@cfxnetwork.com 2022 NOVEMBER VOL.111. NO.11 Skillings Mining Review of CFX Network LLC, publishes comprehensive information on global mining, iron ore markets and critical industry issues via Skillings Mining Review Monthly Magazine and weekly. SMR Americas, Global Skillings and Skilling Equipment Gear newsletters. SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW (ISSN 0037-6329) is published monthly, 12 issues per year by CFX Network, 350 W. Venice Ave. #1184 Venice,
Phone:
x
Printed in the
Payments
#1184,
Periodicals Postage Paid at: Venice, Florida and additional mail offices. Postmaster: Send address changes to: Skillings mining review, 350 W. Venice
#1184 Venice,
Phone:
444
x 4. Fax:
Email: Advertising@Skillings.net. CUSTOMER SERVICE/ SUBSCRIPTION QUESTIONS: For renewals, address changes, e-mail preferences and subscription account status contact Circulation and Subscriptions: subscriptions@Skillings.net Editorial matter may be reproduced only by stating the name of this publication, date of the issue in which material appears, and the byline, if the article carries one. www.skillings.net 4 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022
is supported by these leading providers of materials, services and supplies to the mining industry. Please



whenever possible and let them know you
in Skillings.

Skillings Mining Review
patronize them
saw their advertisement
ME Elecmetal NAYLOR PIPE www.skillings.net | 5
Comminution Solutions
With over 100 years of experience in mining and metallurgy, we align with the priorities of our customers, positioning ME Elecmetal as a true strategic partner in mining.
Integral Solutions Add Value


Mill Liners:
ME Elecmetal is the world leader in designing and supplying highly engineered mill liners and total liner solutions for SAG, AG, ball, tower and rod mills.



Grinding Media:
ME Elecmetal designs, manufac tures and supplies the highest quality forged steel grinding media for SAG, ball and rod mills.

ME Elecmetal’s ME FIT System® programs are aimed at continuous improvement through Research + Development + Innovation, carried out by a multidisciplinary group of professionals with mutual collaboration between the client and ME Elecmetal. The programs involve several initiatives, that together, aim to solve challenges and uncover opportunities to positively impact our client’s key performance indicators: productivity, reliability, availability, safety, e ciency and / or energy consumption.
Crusher Wear Parts:


ME Elecmetal o ers wear parts for all makes and models of primary, secondary, tertiary and pebble crushers. Technology:
ME Elecmetal also o ers 3D laser scanning, liner design and engineering services, discrete and nite element modeling and mill and crusher optimization services as part of our extensive service portfolio.
We consider all factors a ecting the grinding processes. We collect operational data including processed tonnage, available power, down time, load levels and all other relevant information about how our customers’ mills operate. We measure how long media and liners last, what production levels they are achieving and what opportunities there are for improvement in the comminution process.





At ME Elecmetal, we align with the priorities of our customers, positioning ME Elecmetal as a true strategic partner in mining.

P

Premier Product Lines
that exceed the expectations of our customers
Innovation that Creates Value



Solutions
ME Elecmetal analyzes customer operations to determine the ideal combination of design and materials to achieve the optimal performance of their equipment. Whether it is an AG, SAG, ball, tower or rod mill, our innovative liner and alloy designs deliver proven performance, while minimizing costly downtime. We work closely with our customers on the frontlines to identify opportunities for improvement. We adapt to challenges as they arise and o er solutions to positively impact priority KPIs.

ME Elecmetal Minneapolis, MN • Tempe, AZ 763-788-1651 • 480-730-7500 www.me-elecmetal.com

to positively impact priority KPIs













www.skillings.net | 9
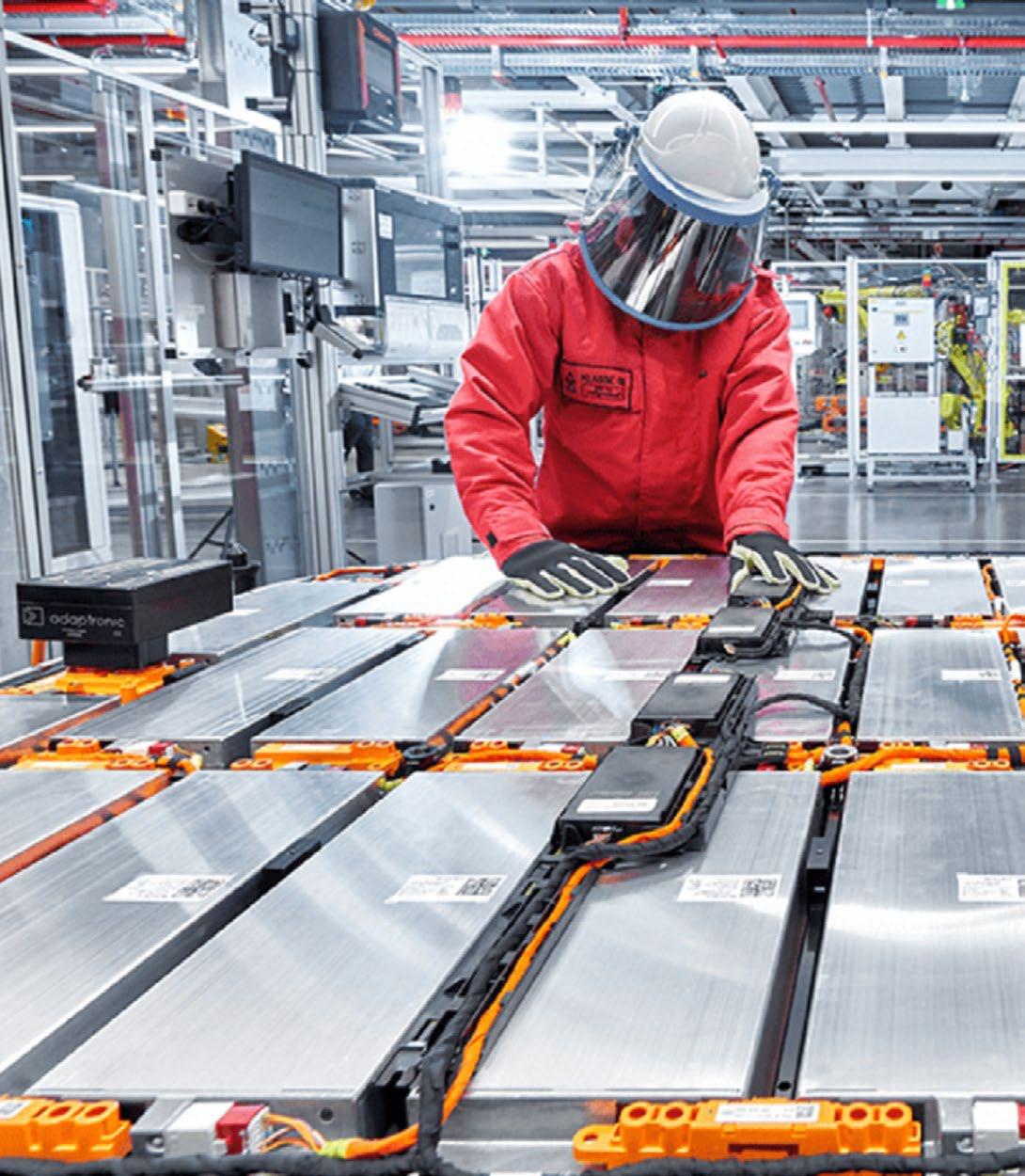
Sandvik Needs To Be Applauded In Underground Mining Established A New and Commendable Battery System Safety Standard
The TasTe and need for baTTery elecTric vehicle (bev) soluTions in The mining industry have increased tremendously in the 3.5 years since Sandvik bought Artisan Vehicle Systems. From discussions that were primarily focused on North America and concerned the testing of BEVs, the industry has advanced to talk about commercial, fleetsized applications that will be implemented all over the world.
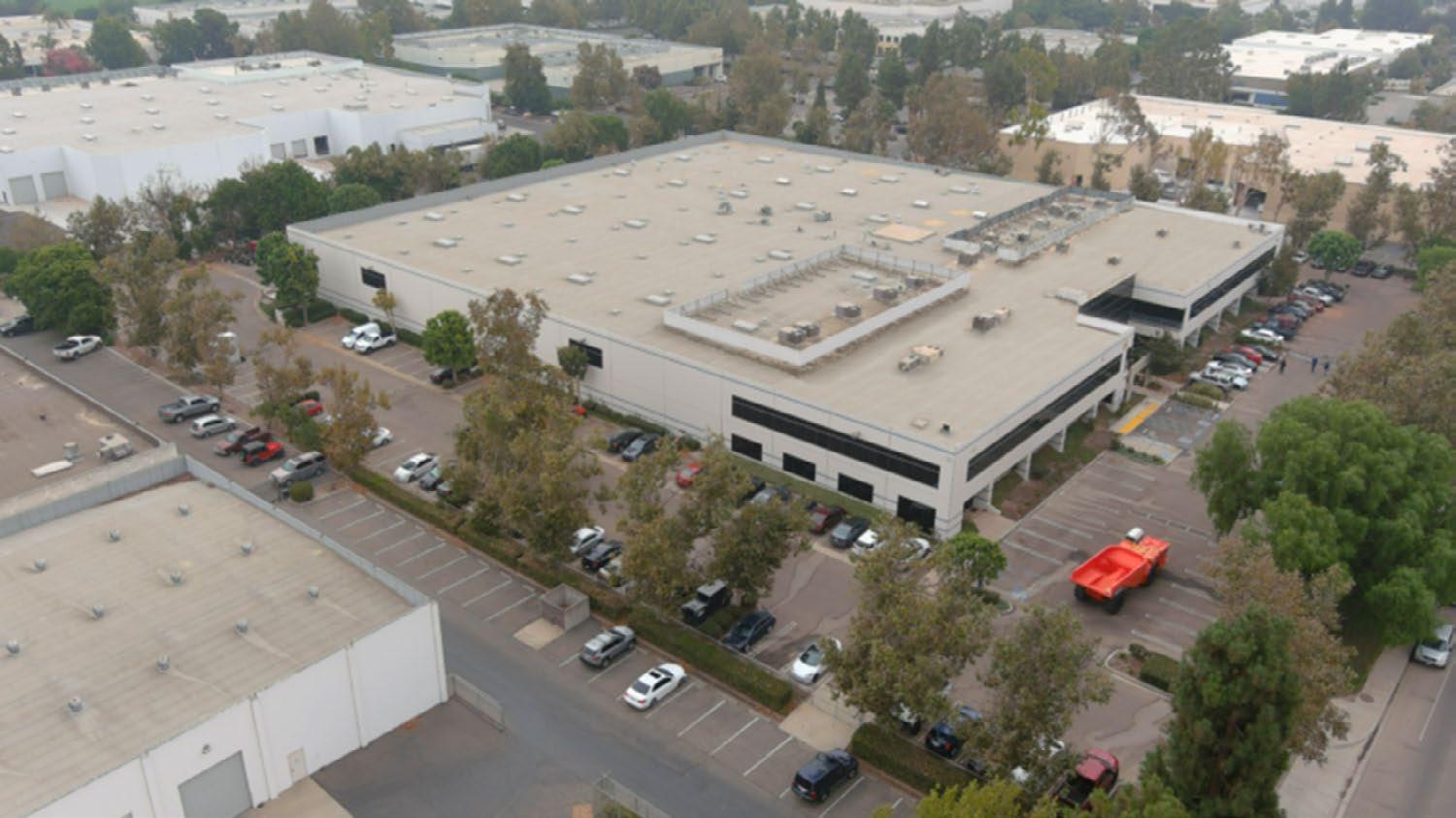 "Sandvik's state-of-the-art battery system facility in Camarillo, California, boasts 100 MWh of annual battery production capacity, as well as acting as a
"Sandvik's state-of-the-art battery system facility in Camarillo, California, boasts 100 MWh of annual battery production capacity, as well as acting as a
training and customer
visitor center
with a test
ramp
that has a 20%
grade
and a whole
area for mucking on the property"
10 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022 THE LEAD
W
ith the award of its largest BEV contract to date—a 20-piece equipment order from Canadian company
Foran Mining—Sandvik itself emphasized this in July. The industry's increased emphasis on underground electrification using batterypowered machinery has also raised the volume and complexity of concerns around battery system safety.
(BHEV) Battery and Hybrid Electric Vehicles
Business Unit of Sandvik Mining and Rock Solutions is more than ready to conduct these discussions, according to Jakob Rutqvist, the unit's VP of Strategy and Commercial.
As an early adopter, "it's up to us to dis seminate the lessons learned and assist the industry in educating itself regarding battery safety and engaging with the stakeholders involved in the supply chain," he said.
Over the past few years, Sandvik has operated BEVs in mining for hundreds of thousands of hours with the aid of Artisan.
The Artisan battery system architecture, which has been developed to adapt to both mining market demands and battery tech nology, has provided support for this.
“In addition, we create in-house battery systems, which gives us a lot of control over the design”, says Brian Huff, Vice President of Technology for the BHEV business unit. “Compared to an OEM that uses batteries made for automotive or industrial applica tions, where those bigger quantities tend to drive design decisions, we can be much more responsive to the market in terms of making modifications to the design.”
"We don't have that divergence of attention; we act in a mining-appropriate manner."
Sandvik invested in a cutting-edge battery system plant in Camarillo, California, with a 100 MWh yearly battery production capa bility, as a result of doing what is "good for mining." With a test ramp that has a 20%
grade and a large area for mucking on the site, this same building serves as a training and customer visitor center.
Regarding the latter, Huff stated: "We will test every product that leaves the shop and undertake a lot of development work — as a result, our development cycle has sped up." Additionally, as part of its commitment to the mining industry, Sandvik invested in a battery system platform that, in terms of safety, considers the challenges of operating machines in underground mines.
Right Chem Quality Cells
Starting at the cell level, Sandvik's battery system has an inherent level of safety. To secure a steady supply of high-quality battery cells that would easily fit into its battery system architecture, Artisan teamed up with China-based CALB back in 2015. After seven years, half of which were spent pretending to be Sandvik, Huff finds no reason to alter his ways.
Consistency and high-quality cells are important for battery system safety, he noted. "That is accomplished through high-volume production coupled with automation and quality production controls. "CALB, which manufactures several batteries for buses and stationary applications both in China and internationally, has completed all compliance and testing on its cells and satisfies all safety criteria." The battery cell manufacturer was also a pioneer in the development of lithium iron phosphate (LFP)-based batteries, and Huff is keen to highlight the advantages of adopting such battery chemistry in terms of safety.
Huff states, "Our approach to battery safety, which is a component of the standardised Sandvik method for safety with ISO and other standardisation bodies, is to look, first, at minimising the severity of a potential incident or removing the hazard. For us, lowering the severity of a thermal runaway entails making a chemical decision.”
www.skillings.net | 11
When the temperature inside a battery increases to the limit that a chemical reac tion starts occurring inside the battery, a chain reaction known as thermal runaway takes place. This chemical process gener ates heat, which raises the temperature and prompts other chemical reactions and heat production. Batteries may melt, become irreparably damaged, or, in extreme cases, ignite and start fires due to excessive heat generation at a rapid rate.
Thermal runaway preventions are frequently the first item battery companies highlight in safety briefings due to their propensity to result in such an occurrence.
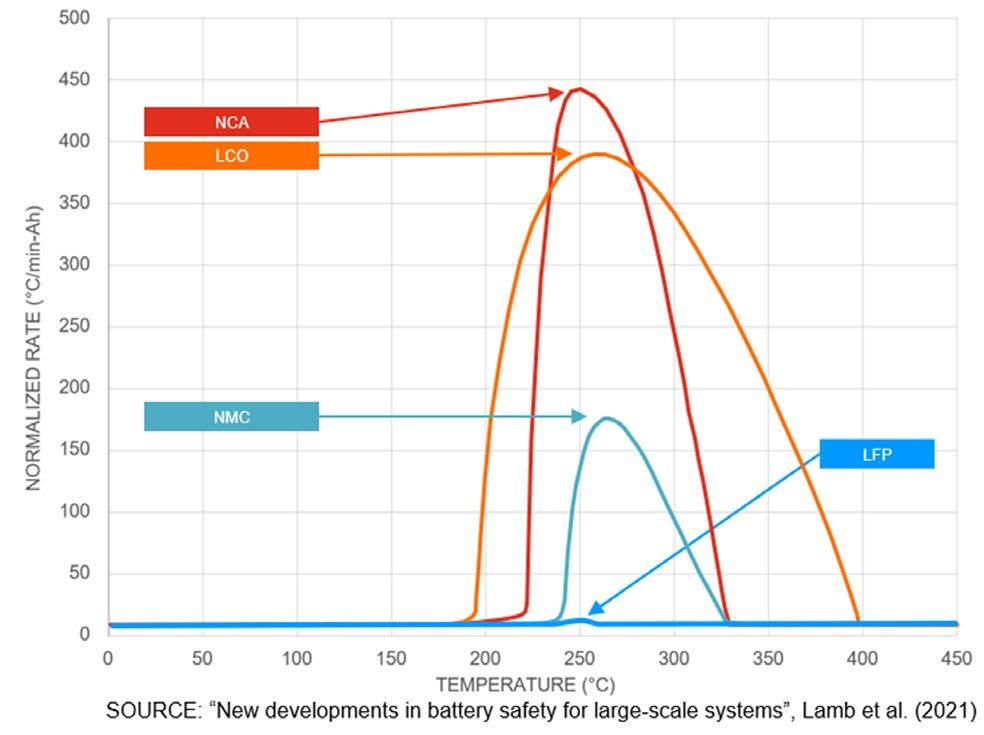
It is simple to illustrate Huff's point when the main commercial battery chemistries are plotted against the heat-release-rate (HRR) on a graph (see graph below). According to Sandvik, the rate of temperature rise (HRR) measures the severity of a thermal event; the higher the HRR, the more difficult it is to contain an incident.
In light of all of this, the company claims that containment is more feasible due to the LFP's rate of temperature rise, which is over 100 times lower than that of other batteries with chemistries like nickel-manganese-co balt (NMC), lithium-cobalt oxide (LCO), and lithium-nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA).
LFP-based cells have released a flammable gaseous electrolyte during thermal runaway testing, but they do not self-ignite during con ventional safety tests, according to Sandvik.
The safety advantages of employing LFPbased batteries have also been emphasized in tests on batteries looking at the produc tion of toxic pollutants. Compared to far greater levels generated from NMC- and lithium-ion-manganese-oxide (LMO)-based batteries, emissions of substances such as carbon monoxide, nitrous oxides, and hydrogen fluoride were modest, according to a US CDC nail penetration test.
PASSIVE SAFETY, INTRINSIC SAFETY
In terms of safety measures, the battery chemical selection falls under the category of "severity reduction," but Sandvik's approach to battery system safety goes further than that.

The risk of the hazard occurring is then decreased by design controls, according to Huff. This is where engineering steps in; the best design controls are frequently passive and intrinsic, implying you need not take any action in the occurrence of an incident. Starting in the cell, Sandvik's locker contains numerous such controls.
High-reliability vents on the cells in Sandvik's battery systems minimize pressure build-up in the event of thermal runaway. The firm claims that this removes the possibility of a case rupture or burst. Additionally, they include a laser-welded aluminum casing with insulation made of mylar and polycar bonate that provides mechanical safety and thermal conduction.
In contrast, a shutdown separator coating is intended to melt if the interior of the cell exceeds 110–130°C. This will stop the pas sage of ions, stop the current, and stop the temperature from rising further. In order to restrict dendrites and give structural support to avoid shrinkage and maintain the separation of the electrodes, a second porous ceramic separator coating that melts at 160–175 °C and bonds with a polypropylene electrode separator is needed.
Huff elaborates, saying that dendrite forma tion is a result of excessive current, charging too quickly, charging in cold conditions, and aging. Additionally, excessive growth has the potential to cause an electrical short, which could trigger a thermal runaway.
According to Sandvik, these cells are put into a battery module that runs at low volt age for safe servicing, has isolating foam potting to block moisture and prevent
"In Sandvik's battery system design, a battery cell (far left) is placed into a battery module (second from left), which is then incorporated into a battery pack (second from right). This pack is then enclosed in a cage (far right)."
Sandvik invested in a cutting-edge battery system plant in Camarillo, California, with a 100 MWh yearly battery production capability, as a result of doing what is "good for mining."
12 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022 THE LEAD
HALCOR PRODUCTS
Copper tubes with or without lining or industrial insulation for applications in:
• Drinking water and heating networks
• Underfloor heating and cooling
• Gas and medical distribution networks gases
• Cooling and air conditioning systems
• Solar energy applications
• Various industrial applications
Halcor is the copper tubes division of ElvalHalcor S.A. and together with four more companies form the copper segment of ElvalHalcor S.A. that specializes in the production, processing and marketing of copper and copper alloys products with dynamic commercial presence in the European and global markets. For more than 80 years, Halcor has been offering innovative and added-value solutions that meet contemporary client demands in fields, such as plumbing, HVAC&R, renewable energy, architecture, engineering and industrial production.
The copper segment of ElvalHalcor S.A. is composed of six subsidiaries and seven associates/joint ventures, based in Greece, Belgium, Bulgaria, Romania and Turkey, while it operates a total of five production plants in Greece, Bulgaria and Turkey.
The copper segment of ElvalHalcor S.A. develops and distributes a wide range of products, including copper and copper-al loy rolled and extruded products with Halcor being the sole producer of copper tubes in Greece. High quality in production

is achieved through strict controls applied throughout the production process. With a consistent quality focus, the company implements an ISO 9001:2015 Certified Quality Management System and leverages high technologies and expert staff.
As a result of the Group’s strategic invest ments in research & development, Halcor is recognized as one of the leading copper producers globally, setting new standards in copper processing. The company main tains a consistent focus on quality and

environmental protection and a strong commitment to the principles of sus tainable development. In this context, all production facilities in the Group’s plants leverage advanced technologies to bring in the market innovative products that are energy efficient and environmen tally friendly.
For more information, please visit our web site www.halcor.com
www.skillings.net | 13
isolation faults, and offers thermal con duction to transfer heat from a hot cell and distribute it throughout the entire module to reduce temperature rises, and provides protection against mechanical and environ mental damage.
Then, these modules are integrated into a battery pack, which has mechanical safeguards like a 6-mm steel enclosure, a non-conductive coolant to regulate tem perature during charging, and gore vents and drains to prevent pressure build-up. These safeguards allow vented gases to expel air in the enclosure and fluids to drain rather than collect, all of which limit the entry of dust and contaminants.
According to the business, the redundant design of the battery pack contactors enables the circuit to be severed in the event of an over/under voltage, isolation fault, over tem perature, or over current. A high-voltage interlock loop (HVIL) system might also do this. Last but not least, the addition of 600 A fuses offers defense against overcurrent and harm from exterior shorts.
The battery pack is also housed in a cage, which according to Sandvik, provides strong mechanical protection, mobility, and swap pability. It also allows for easy access to the pack modules without requiring the disassembly of the cage.

Post Design Designs
We begin with the presumption that design controls, no matter how effective, should never be thought to be 100% effective, according to Huff. "For example, you cannot simply address the problem by ignoring the possibility of thermal runaway. It isn't realistic, especially in a mining context where damage, accidents, and human error can happen.
This prompts the business to discuss the active controls that are part of its bat tery system.
Monitoring is the beginning of it all, Huff added. It might examine voltage and tem peratures, including case temperature, terminal temperature, and conductor temperature.
The Battery System Controller (BSC) calcu lates the limits and thresholds, monitors the
HVIL, isolation, temperature, and currents, connects the battery, and communicates the status. However, the system is not responsi ble for putting the controls and restrictions into place.
The master controller unit (MCU) is in charge of achieving those restrictions, according to
"Embedded" monitoring software on the battery and "remote health monitoring" applications are the first development priorities post-integration.
14 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022 THE LEAD
Huff. "The battery system controller commu nicates what the limits are, such as only 400 A in discharge owing to the heat, for example.
As a last option, the battery system controller opens its connectors and disconnects power if the MCU is unable to do so (for example, by drawing too much current).
The battery monitoring system (BMS) con trols cell balancing, regulates cell voltage and temperature (including case, terminal, and conductor temperatures), and transmits information to the BSC.
Akkurate, a battery analytics company that Sandvik acquired earlier in the year and its remote battery diagnostic and prognostic platforms will be integrated into the BHEV business unit, further enhancing this moni toring. Although you can often reduce external dangers, Huff stated that such monitoring can only go so far in assuring safety from within the system. In terms of electrical fail ure modes, he said that monitoring-based functions may help prevent overcharging and over-discharging but couldn't shield against deformation, mechanical harm, or intrusion from external objects.
This is where the "suppression" compo nent is relevant. For its fire suppression system, Sandvik uses a chemical emulsion with a potassium base that is electrically non-conductive. It works by injecting an aerosol agent into the battery pack interior, which chemically prevents combustion and halts a possible fire in its tracks.
"These suppression systems came in and did the job we prescribed for them in a couple of previous occurrences, which were minor," Huff said. They are not intended to put out a widespread battery fire; rather,
Equipping the mining industry with legal services since 1893.

purchase agreements,
and options
assembly and
rights
mineral registration
title work
permitting
fryberger.com
›› Paul Kilgore ›› Paul Loraas ° MINING & MINERALS LAW ° ∙ Mineral
leases
∙ Land
mineral
acquisition ∙ Severed
and
∙ Environmental
and compliance
www.skillings.net | 15
the safety barriers are the chemistry choice and the additional passive controls we have built-in.
All Stones Unturned
According to Huff, the company frequently looks beyond industry standards and regulations when designing features in, which is shown in the company's threestep safety process and its emphasis on risk reduction for its clients.
According to him, "the volume and value proposition of our products affect the needs for battery system design." "We're not attempting to cut costs here by, say, reducing enclosure thickness or changing a design element to be more cost-effective.
"Safety and dependability are far more cru cial than how much it costs to make the system," On board its battery systems, there are numerous instances of this safety-de sign-over-cost mentality. For instance, to reduce the risk of an electrical short, the company has minimized the usage of wires and designed as much as feasible with bus bars. The live conductors won't be engaged
by any "casual" contact from operators or service professionals because all of these busbars are powder coated and electri cally shielded.
The business has included safety measures when it comes to monitoring isolation. In the beginning, isolation monitoring for battery systems was required to warn technicians of the risk of an electrical shock in the event of an isolation problem, according to Huff.
In addition, it can serve as a precursor to a greater current short circuit when an iso lation fault occurs with a resistance below a specific threshold. After conducting some investigation, Huff and his team determined that 5,000 ohms was the proper threshold for this specific risk.
"You can create a short circuit with enough power to melt some of the protective mate rials in the battery system and potentially accelerate this to a much higher current short circuit," the expert explained. "If you have a 5,000-ohm isolation fault in a location and have a direct connection from another point to the chassis."
Differentiated action is necessary for response to this second isolation monitor ing factor.
He explained that shock hazards are a warn ing condition in which people need to be made aware of the danger and instructed to act differently. A short circuit risk, also known as a low impedance isolation issue, requires a different approach. For us, this entails either finding the defect and shifting the modules to isolate the fault or shutting down the unit and doing so. The business can accomplish this because Artisan battery systems are made to be disassembled into individual batteries and carried separately as needed.
Over the past five years or so, "a few battery fires reported in mines, involving various sorts of equipment," Huff added. The two that I am aware of had everything to do with isolation issues and nothing to do with a BMS reaction. Therefore, a crucial factor is how you treat a battery in this situation.
Advantages of backward compatibility Huff, a co-founder of Artisan, can contextualize the mining offer more effectively than most due to his experience electrifying heavy-duty commercial vehicles and the automotive industry, two industries that Artisan served before focusing on underground mining.
The required level of serviceability, he noted, is a crucial distinction. "Mining is a very dif ferent world; you are so far removed from a tidy business with everything you need and room to work. Mining does not have the same infrastructure that is available for vehicles.
"At mine sites, there is a lot of pressure to complete the work on-site using the tools you have with you. If you don't have the specific tool, you usually make do without it or invent one. You must have a product made

(BHEV) Battery and Hybrid Electric Vehicles Business Unit of Sandvik Mining and Rock Solutions is more than ready to conduct these discussions, according to Jakob Rutqvist, the unit's VP of Strategy and Commercial.
16 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022 THE LEAD
specifically for that setting, and we have done just that. The standardization and commod itization of Sandvik's battery systems occur at the cell level, leaving the company flexible to adjust and customize in response to the needs from the mining industry.
Mining clients "count in hundreds, not thou sands, if you take the market at a battery system level," he said. "Our largest custom ers are quite huge, and they want to have a say in the development and specifications for the battery system. Our typical client is substantial, and they expect to be very close to us when it comes to product and the product development.

"We don't want to be intermediaries for the battery system design, but we're pleased to be middlemen for the battery cell." This has made it possible for the business to benefit from advancements in battery technology as they have happened over the previous several years and moving forward.
At the Macassa gold mine in Ontario, Canada, which has one of the largest battery-electric fleets in the world, Haley-Anna Blinn, who is currently a BEV Applications Specialist at the Sandvik BHEV business unit, has been on the receiving end of this.
"The battery space is changing so much all the time," she added. "Despite my short involvement of barely five years, I have wit nessed significant progress. "We understand this, so it's critical that we design our systems to support future design modifications or even battery chemistry advancements in terms of energy density.
"With the older models of equipment, there was once a switch in the cell supplier, which led to cells with a different form factor. "While this adjusted the number of cells in a module according to their characteristics, the adjust ment was made without any noticeable disruption when the cells were scheduled for refreshment. From the standpoint of battery
system design, the module was backward compatible due to its identical form factor.
According to Blinn, the new cells also man aged to boost performance by roughly 20%. The Sandvik BEV customers could be in line for comparable step-change improve ments in the future given the average battery cell life of 3-5 years, battery performance continuing to advance exponentially over a similar timeframe, and the internal funding resources of the Sandvik Group.
The business can also make more subtle adjustments to its battery systems based on the current functioning.
Technicians may modify the system at the factory to the conditions they will probably encounter underground by using sophisti cated modeling software and a databank that dates back to the beginning of Artisan's BEV voyage. This goes beyond just restricting the speed to safeguard the battery system and
the drivers. “We may set these settings at the manufacture since, depending on the duty cycle, some mines may be better suited to a slower charge than others, according to Blinn. According to the operational conditions underground, some mines might impose a temperature limit that exceeds the preset limits we program. To ensure that the system operates differently during operation, we can make those changes.”
Since the obvious teething issues with the introduction of BEVs at underground mines have been resolved over the past decade or so, Sandvik is entering a consolidation period where minor adjustments to the system design will be made rather than complete overhauls. The company's min ing-focused, safety-conscious battery system design philosophy continues to set it apart at a time when mining companies demand improved performance and uptime from these machines to meet their own electri fication and productivity goals.
www.skillings.net | 17
NioCorp CEO: Do Not Count On China For Rare Earth Metals

Because China is increasingly using its own production for electric vehicles and other technologies that use permanent rare earth magnets, automotive and other manufacturers should not rely on adequate supplies of rare earths and oth er critical minerals coming from China, according to Mark A. Smith, CEO and Executive Chairman of NioCorp Develop ments Ltd. Mr. Smith appeared on Liz Claman's "The Claman Countdown" on Fox Business News.
The piece was broadcast on foxbusiness. com on October 3, 2022. The majority of the rare earths produced now in the globe come from China, according to Mr. Smith, who emphasized the importance of rare earth minerals.

"That's wonderful, but China produces a tonne of electric vehicles. We now want to manufacture EVs. Furthermore, we won't be able to power all of our desired electric vehicles with the rare earths that are coming from China."
When enough project funding is found to allow the Project to move forward, Ms. Claman asked Mr. Smith if significant automakers and other possible clients are inquiring about the essential minerals that NioCorp wants to produce at its Elk Creek Critical Minerals Project in south east Nebraska.
"Who's coming up to you now? Who is seek ing these minerals? Has word spread?" Miss Claman enquired.
The reply from Mr. Smith was, "The word is out. "You may have seen reports about the steel and automobile industries going out and looking for these minerals. These minerals
Mark A. Smith, CEO and Executive Chairman of NioCorp Developments Ltd.
18 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022 RARE EARTH
are hard to come by. We are currently in conversations with some of the world's big gest steel and automotive businesses because they want to develop their procurement plans over the course of 10, 15, or 20 years. We're eager to speak with them."

Additionally, Mr. Smith offered his thoughts on NioCorp's recent news that it had signed a binding contract (the "Business Combina tion Agreement") for a proposed business merger with GX Acquisition Corp. II ("GXII") (Nasdaq: GXII). NioCorp intends to list on the Nasdaq Stock Exchange shortly after the acquisition closes, which is anticipated

in the first quarter of 2023, in accordance with the Business Combination Agreement, subject to approvals from both the NioCorp and the GXII shareholders at to-be-called special shareholder meetings and other customary closing conditions.
NioCorp will acquire GXII, a U.S.-based spe cial-purpose acquisition company. Shares of NioCorp will still be traded on the Toronto Stock Exchange. The merged entity's esti mated enterprise value under the proposed acquisition is $313.5 million.

Proud to be your reliable
When enough project funding is found to allow the Project to move forward, Ms. Claman asked Mr. Smith if significant automakers and other possible clients are inquiring about the essential minerals that NioCorp wants to produce at its Elk Creek Critical Minerals Project in southeast Nebraska.
www.skillings.net | 19
partner. We have long supported the region’s mining industry by providing safe, reliable and competitively priced electricity. In 2021, half of the energy we provide to all of our customers will come from renewable sources. Together, we power northeastern Minnesota’s economy. mnpower.com/EnergyForward 19260
Job Growth In Coal Counties: VTS Targets Confirmed

When it comes to the goals of its job creation and investment activities, the Virginia Coalfield Economic Development Authority is on the right track, according to a study it commissioned.

T he Virginia Tech Center for Economic and Community Engagement report makes the suggestion that VCEDA keep concentrating on the advanced manufacturing, electronic information technology, energy-related businesses, and creative tourist industries.
According to Belcher, the study cost around $25,000. According to him, a North Carolina consulting business conducted a similar study in 2014 with identical findings. Along with two other people, Scott Tate, associate director of the Virginia Tech Center for Economic and Community Engagement, worked on the study. According to him, it took place between February and August. According to him, the center has completed several studies for counties and regional economic development groups.
Results
According to Belcher, one of the analysis's most encouraging findings was that the
region is outperforming national norms in important industry sectors. That was the case in advanced manufacturing, particularly in the production of machinery, fabricated metal goods, and electrical equipment, all of which had growth that was higher than the national average over the previous five years.
According to the research, there were 26 companies producing machinery in the VCEDA region in 2021, which was respon sible for around 800 jobs.
This figure is "126% higher than the national employment average. According to the analy sis, the VCEDA region saw a 23% gain in jobs in this industry from 2017 to 2021, compared to a 3% national decline and a 0% change in Virginia.
Three local businesses that produce machin ery were named in the report: Tadano Mantis Corp. in Richlands, which produces tele scoping boom crawler cranes; Komatsu, which has facilities in Abingdon, Duffield, and Norton and makes construction, mining, forestry, and industrial equipment; and Sim mons Equipment Co. in Tazewell, which produces mining equipment.
CHALLENGES
Belcher claimed that the issue that most caught his attention was the region's lack of sufficient land supply and the scarcity of locations for particular types of enterprises.
MINING JOBS
THE EXECUTIVE DIRECTOR AND GENERAL COUNSEL OF VCEDA, JONATHAN BELCHER, REFERRED TO THE STUDY'S FINDINGS AS "REASSURING."
20 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022
Gold Mining Stocks Bullish Mid

Octoberas The federal reserve embarks on iTs mosT aggressive raTe hiking cycle in recent memory, gold declined for the sixth consecutive month, a losing record we haven't seen since 2018.
In its battle against inflation, the central bank has raised rates by about 250 basis points (bps) so far this year, and numerous asset classes, including equities, bonds, and bitcoin, have suffered as a result.
Gold is no exception, but it has managed to hold up better than most investments despite higher rates and the precious metal's longtime rival, a historically strong dollar. The SandP 500 has currently lost 22% of its value for the year, but gold has only lost 7%.
If you didn't already know it, October has historically been the worst month for equi ties. October of last year did not let down. The SandP 500 lost more than 9% of its value, making October 2018 the worst month overall since March 2020.
The month also saw a collapse in emerging markets, with Taiwan Semiconductor, Ten cent, Samsung Electronics, and Alibaba all experiencing 15%–20% declines.

SOLVING YOUR MOST COMPLEX CHALLENGES. With SEH, you are a true partner and collaborator. Engineers | Architects | Planners | Scientists 800.325.2055 | sehinc.com/subscribe
www.skillings.net | 21
John Robins Joins Gelum
Resources as Advisor
John Robins, P.GEO, has been named as a company advisor, according to Gelum Resources Ltd. Director Henk van Alphen said, "I'd like to extend a warm welcome to John Robins as an Advisor to the Company on behalf of Gelum Resources. We are looking forward to collaborating with Mr. Robins, who brings to the Company 35 years of technical geology, business development, and opportunity .
John Robins, P.GEO. Professional geologist, prospector, and businessman John Robins has more than 35 years of expertise in the mining sector. For his contributions to mineral exploration in British Columbia and Yukon, he received the Spud Huestis medal in 2008.
The Dixie Lake Gold Deposits in Red Lake, Ontario, the 5 million oz. Coffee Gold Deposit in Yukon, the Three Bluffs Gold Deposit in the Committee Bay Greenstone Belt, and the Aviat/Churchill Diamond Districts in Nunavut are just a few of Mr. Robins' famous discoveries. He has generated over $500 million in direct and indirect mining expen ditures throughout Canada, Latin America, and Australia, as well as over 2.5 billion dollars in M&A activity.
Gelum Resources is a Company led by sea soned management and advisors in the mining and financial sectors. The Com pany currently has two objectives under management. The first is to define a multimillion-ounce economic gold deposit on the 9028-hectare Eldorado Gold Project, located within the Bralorne-Bridge River gold district.
Shale drillers Struggle for Workforce
according To a labor deparTmenT sTudy released lasT monTh in October, the job market in the US shale region is getting even tighter as drillers battle to find enough personnel to fulfill output objectives this year.
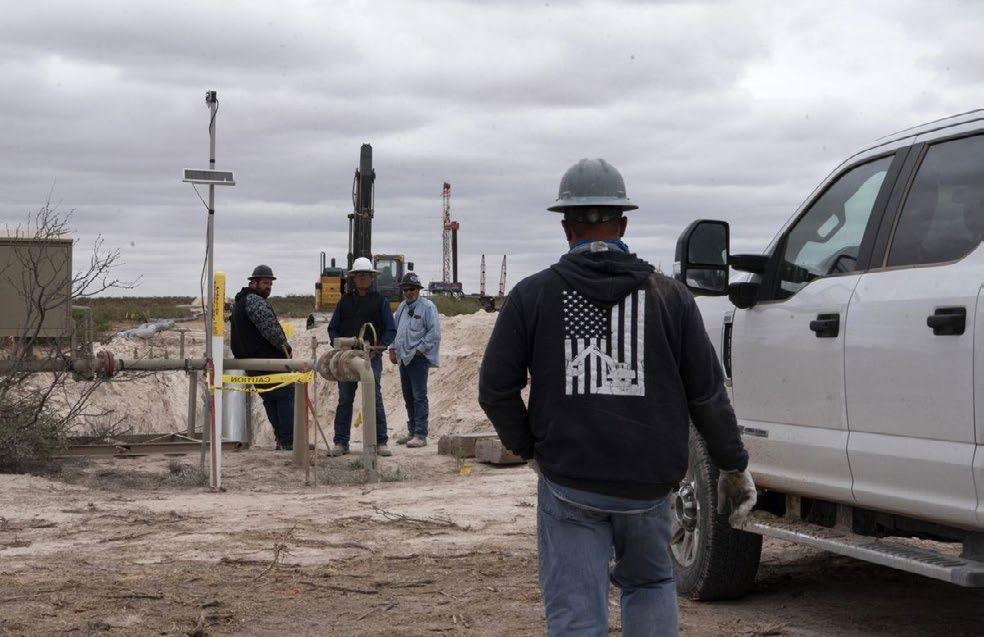

According to official data, the jobless rate decreased to 2.5% in September from 2.6% the previous month. In contrast, a year earlier, there was a 7.3% unemployment rate. Oil corporations are reluctant to drastically increase wages because they want to keep a lid on costs that are out of control. As a result, oilfield workers have been searching for jobs with higher compensation elsewhere, with renewable energy becoming the most sought-after industry. Double-digit yearly wage increases won't be available to workers until 2024, according to industry expert Rystad Energy. Rystad predicted a 2.9% increase in pay this year.
One of the main obstacles preventing increased output is a lack of workers in the oilfield. The Biden administration's effort for greater output in response to OPEC+'s agreement to reduce supply may face extra difficulties if employees are hard to come by to drill and frac new wells. US oil and gas employment reached 133,800 last month, a 4.8% decrease from the year's peak in July.
With a 7.7% decline since February 2020, the larger mining and logging sector, which includes the oil and gas industry, is the sector that is recovering from pandemic employ ment losses the slowest.
MINING JOBS 22 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022



www.skillings.net | 23FloLevel Technologies
Fossil Fuel Growth Vs. Clean Energy’s Progress
according To a number of recenT publicaTions, clean energy is experiencing a surge in new development all over the world, with electricity generated from carbon-free wind and solar power helping to meet expanding global energy demand.

However, as more new fossil fuel projects come online, the advantages of the new renewable energy, especially its effect on greenhouse gas emissions, are being undercut.
The upcoming COP27 global climate talks serve as the latest reminder that fossil fuels
still have a firm hold on the global economy and continue to jeopardize efforts to avert catastrophic climate change by the end of the century. Early indicators suggest that the world is still far from meeting the goals of the Paris Agreement. In reality, study shows that investments in clean energy must treble within the next ten years in order to even
have a hope of meeting the worldwide cli mate accord's Herculean aim of targetting net 0 emissions by 2050 in order to keep average global warming to 1.5 degrees Cel sius. According to the report, investments in fossil fuels continue to exceed those in renewable energy, with around 90 cents of every dollar spent on fossil fuels moving into renewable sources.
As a result, there has been a surge in the con struction of new clean energy infrastructure, which is spectacular but is still unable to stop the upward trend in global greenhouse gas emissions. Government expenses will only rise if this tendency doesn't alter soon.
Over the past ten years, the quantity of electricity produced in the United States from clean sources has tripled. The amount of electricity produced by solar and wind sources increased by 22% in the first nine months of 2022, continuing a trend of record-breaking growth.
However, despite this expansion, the U.S. power sector's emissions have decreased by just 1% so far this year, partly due to a surge in the amount of new natural gas generated coming online at the same time. Similar circumstances are occurring globally, but with coal. The dirtiest kind of fossil fuels has witnessed a rebound in the wake of Russia's invasion of Ukraine, despite recent commitments by governments and the coal industry itself to phase out the usage of coalfired power stations.
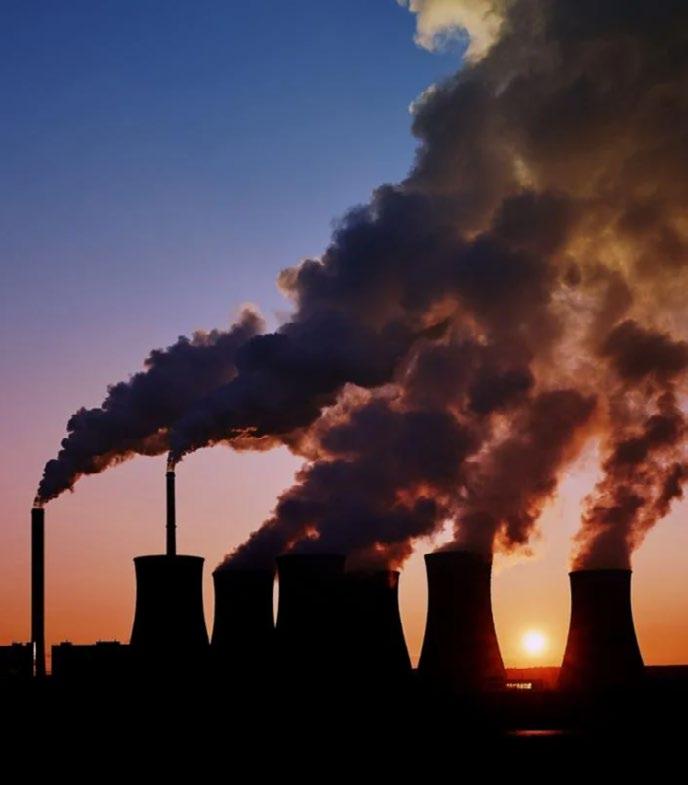

In reality, with China's power sector leading the way, about half of all coal companies in the world currently have expansion plans.
New renewable energy installations more than sufficed to meet the first half of the year's 3 percent growth in global energy demand, avoiding a further 4 percent increase in fossil fuel production and the resulting emission of almost 230 metric tonnes of CO2.
24 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022 SURFACE MINING
SolGold & Cornerstone Merger Transaction
SolGold plc and Cornerstone Capital Resources Inc. announced in October that they had reached a binding agreement under which SolGold will purchase all of Cornerstone's issued and outstanding shares—aside from any that it already directly or indirectly owns—in accordance with a court-approved plan of arrangement.

For every Cornerstone Common Share owned, 15 SolGold Ordinary Shares will be exchanged. As per the Agreement, Sol Gold may choose to pay up to 20% of the consideration in cash. In this case, the cash
would be distributed proportionally among all Cornerstone shareholders, and the number of SolGold Shares that could be issued to Cor nerstone shareholders would be decreased. Existing SolGold and Cornerstone sharehold
ers are anticipated to own roughly 80%, and 20%, respectively, of the combined entity after the Transaction is complete if SolGold chooses not to pay any portion of the con sideration in cash. This is consistent with the current effective exposure of approximately 80/20 to the Cascabel Project at the time of the Transaction.
By combining ownership of the Cascabel Project and a sizable portfolio of other assets, mostly in Ecuador, the Cornerstone and Sol Gold combination will greatly improve the ability of the Combined Group to generate value for shareholders.
www.skillings.net | 25 Industrial General Contractor Specializing in Equipment Installation and Maintenance crmeyer.com 800.236.6650 Offices: Byron, GA Escanaba, MI Muskegon, MI Coleraine, MN Tulsa, OK Chester, PA Oshkosh, WI Green Bay, WI Rhinelander, WI Millwrighting Piping Ironwork Concrete Electrical Building Construction Design/Build Offices Nationwide l l l l l l l Boilermaking l
Latest Uranium/Vanadium district: Advanced exploration: Argentina
blue sky uranium, a pioneer in uranium discovery in argenTina, aims To quickly advance a portfolio of uranium-vanadium prospects to the prefeasibility study stage in order to provide outstanding returns to shareholders. With more than 4,000km2 (400,000ha) of promising tenements, Blue Sky Ura nium Corp. is one of Argentina's best-positioned uranium and vanadium exploration businesses.


26 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022 SPECIAL FOCUS
The goal of the company is to significantly increase shareholder returns by purchasing, pursuing, and promoting a portfolio of uranium-vanadium properties. These initiatives will concentrate on deposits that are close to the surface and could soon yield affordable vanadium and uranium.
In all the places where we operate, the company adheres to worldwide standards for exploration while preserving the envi ronment, local populations, and cultural traditions.
South America's greatest user of nuclear energy for the production of electricity is Argentina. The nation is aiming to build
more nuclear power reactors, although at the moment there is no domestic uranium production. Argentina's quest for supply security may offer a new local supplier a "assured" first customer. Argentina might become a key exporter of uranium to the global nuclear energy industry through largescale production.
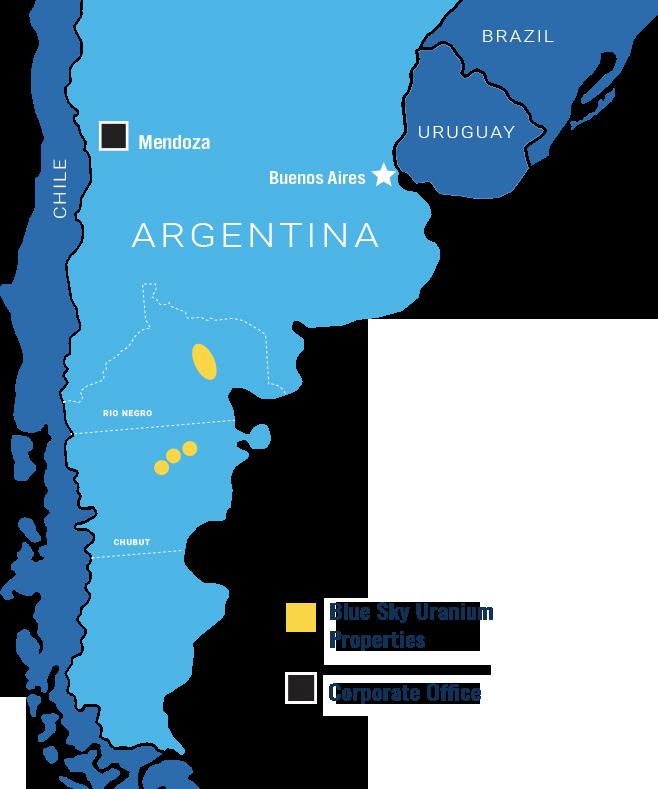
The exploratory effort conducted by Blue Sky between 2007 and 2012 resulted in the finding of a new uranium district in the province of Rio Negro. The Ivana near-sur face uranium deposit, which has the largest NI 43-101 compliant uranium resource in the nation and offers prospective vanadium credits, is one of three main sites included

in the company's Amarillo Grande Project, which spans the district. The project area contains further exploration possibilities for blind vanadium and uranium deposits. Ama rillo Grande is a strong candidate to become the first short-term uranium producer in Argentina due to the proximity of the assets and targets, which offers the possibility for an integrated, affordable uranium-vanadium production operation.
The business is a part of the Grosso Group, a resource-focused management organisation that has been active in Argentina since 1993 and helped to establish the mining explora tion sector there. The company is recognised with discovering four remarkable mineral
www.skillings.net | 27
deposits, and it is well known for cultivat ing close ties with the local governments and communities in which it operates. The exploratory team is supported by The Grosso Group's extensive network of domestic, foreign, and local industry contacts as they look for promising resource prospects.
Focus Amarillo Grande Project's property
The Ivana deposit has an inferred resource of 22.7 million pounds of U308 and 11.5 million pounds of V2O5 (28.0 million tonnes averaging 0.037% U308 and 0.019% V2O5 at a 100ppm uranium cut-off); the preliminary economic assessment (PEA) was completed in 2019; the Ivana deposit is still open for expansion; and exploration is ongoing.
Location
The Amarillo Grande Project is situated in the Patagonia region of southern Argentina, in the heart of the Rio Negro Province. Major cities like the provincial capitals of Viedma or Neuquén can reach all of the properties via road. About 25 kilometres (km) north of Valcheta City, where Blue Sky has a permanent exploration camp/office, is where the Ivana deposit is found.
The city is situated at the intersection of National Road 23 and Provincial Road 4, where the latter connects to the 120 km to the east deep ocean port of San Antonio Oeste. National Road 23 is paralleled by a railroad, and two high-power lines cut across the construction site from east to west.
Investigation and Discovery
Since the start of the revived work programme in 2016, surface exploration, ground geophysics, pit sampling, and more than 9,000m of drilling have been conducted. The business revealed its initial mineral resource estimate for the Amarillo Grande Project on March 5, 2018. The company finished its mineralogical, metallurgical,
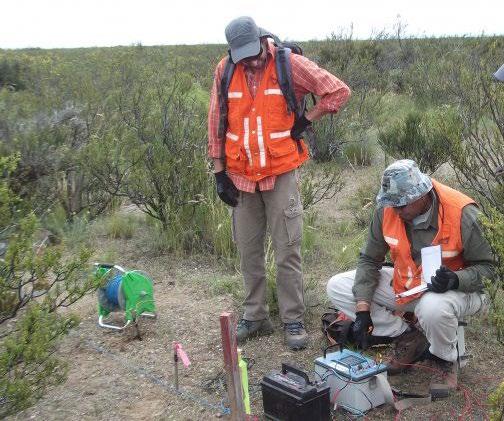

Amarillo Grande is a strong candidate to become the first shortterm uranium producer in Argentina due to the proximity of the assets and targets, which offers the possibility for an integrated, affordable uranium-vanadium production operation.
and process test work while continuing its exploration operations. Blue Sky revealed the first PEA for Ivana as well as an updated resource estimate on February 27, 2019.
At similar grades, the resource estimate accounted for a 19% increase in contained U3O8 and a 13% increase in contained V205. According to the PEA, the mineral resources at the Ivana deposit have the capacity to sustain a surface mining operation with 13 years of vanadium and uranium production.
The bottom half of the Ivana deposit has ura nium mineralization that is more primary in type, which accounts for a sizeable share of the existing reserve. ß-Coffinite is the main
mineralization, along with carnotite, tyu yamunite, liebigite, and pyrite. Mineralization is primarily seen in sedimentary rocks that are weakly cemented and carbonaceous in colour. This mineralization resembles ura nium deposits hosted by sandstones in other parts of the world, especially basal-channel sandstone-hosted uranium deposits, and it appears to be connected to a redox border with potential regional significance.
Examples of this sort of mineralization can be found in the Chu-Sarysu and Syrdarya Basins of Kazakhstan, the Powder River Basin of Wyoming, the Coastal Plain of Texas, and the US, where mappable redox limits have been followed for hundreds of kilometres and
SPECIAL FOCUS
Blue Sky Uranium's geophysics team conducting an Induced Polarisation survey at the company's Amarillo Grande uranium-vanadium project in southern Argentina. Credit: Blue Sky Uranium.
28 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022
contain many deposits of this kind. This sort of uranium deposit can grow to enormous levels, as is the case at Inkai, Kazakhstan, where the known and probable reserves total roughly 244 Mlbs of U3O8 (352kt at a grade of 0.03% U3O8; www.cameco.com).
Investors are advised that there is no guarantee that deposits on the Blue Sky properties will be the same amount or quality as these deposits. The competent person has not independently verified the veracity of the information regarding these thirdparty deposits.
The business has maintained extensive exploration efforts while also finishing mineralogical, metallurgical, and process test work since issuing its first resource estimate on March 5, 2018. According to information released on February 27, 2019, this work was incorporated into an updated resource estimate and the initial PEA for Ivana. approaching a prefeasibility analysis.

2022 Great Lakes Marine Hall of Fame Inductees
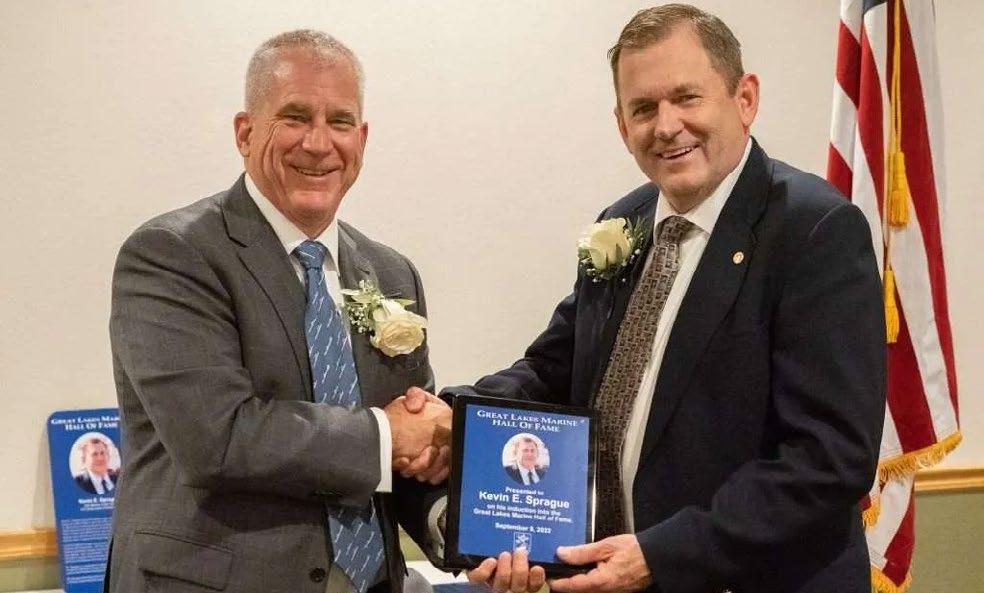

The saulT hisToric siTes, capTain John p. WellingTon greaT Lakes Marine Hall of Fame, recognized the significant contributions of two Great Lakes maritime members today onboard the Museum Ship VALLEY CAMP in Sault Ste Marie, Michigan.
The Sault Historic Sites, Captain John P. Wellington Great Lakes Marine Hall of Fame, recog nized the significant contributions of two Great Lakes maritime members today onboard the Museum Ship VALLEY CAMP in Sault Ste Marie, Michigan. The Mariner of the Year awards honoured Mr Kevin Sprague and Captain Paul LaMarre, Jr. The award is given every other year alternating between U.S. and Canadian nominees. Mr Sprague served the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers for 30 years, most recently as the Soo Area Engineer for the past 12 years, until his recent retirement in June 2022. He not only oversaw the daily operations of the Soo Locks, he managed the badly needed asset renewal projects on the Poe Lock and led the beginning of the new large lock construction.
Captain John Wellington, who gave Kevin’s introduction speech, said, “Kevin Sprague led the team at the Soo Locks during challenging times. His impact will benefit our nation, region and industry for generations.” Kevin Sprague noted, “I am grateful for the award and the recognition it brings to me and the many dedicated and talented women and men working for the Army Corps of Engineers at the Soo. Cargo moves because of you.”
Capt. LaMarre Jr. has followed in the footsteps of his great uncles Frank and William Hoff man, both masters of Great Lakes freighters in the early 1900s. Through his position as the corporate treasurer and a captain for the Gaelic Tugboat Co. and Diamond Jack’s River Tours for over 45 years, he has touched nearly every aspect of the Great Lakes Maritime trade.
www.skillings.net | 29
Lithium Mining in North America
liThium is The lighTesT meTal knoWn and iTs capaciTy To reTain energy makes it appealing for use in batteries. To compete with Chi na’s dominance of the electric vehicle battery chain, North America requires lithium mines.
has had various owners, and some of them have filed for bankruptcy. Hence, people are skeptical of its production potential especially since mining and processing materials for electric vehicles is a difficult process. Lithium mining is no exception to this rule.
Some businesses lack the expertise required to blast ore, haul it out of the ground, and separate the lithium from the encircling rock thereby resulting in delays and cost overruns. Extraction of lithium can be extremely diffi cult because lithium deposits are embedded in other metals and minerals.
More refineries in North America are needed to process raw lithium into a concentrated type of metal that goes into batteries. China currently dominates the processing of crit ical metals required by EVs and renewable technologies. Lithium processing also neces sitates expertise, which is scarce in the United States and among the country’s allies.
The Biden climate/tax bill, known as the Inflation Reduction Act, was signed into law in August and included incentives and subsidies for car buyers and automakers. To be eligible for the subsidies, which total more than $10,000 per electric vehicle, battery manufacturers must use raw materials from North America or a country with which the US has a trade agreement.
As bankruptcies and environmental concerns stymie new mine openings, there are some clear candidates but no clear winners. Despite having more than 3% of the world’s reserves, the United States has only one lithium mine producing 5,000 tons per year — less than 2% of the world’s annual supply. Several new lithium mines in Nevada have been impeded by environmental lawsuits for years. Other states in the United
States – including California, Oregon, Tennessee, Arkansas, North Dakota, and North Carolina – have lithium deposits but no clear direction to production.

Even Maine has a deposit which is said to be one of the richest grade ores in the world. A lithium mine owned by the Australian company Sayona Mining is set to open in Quebec, Canada, early next year. The mine
This creates a strange dilemma. Despite the fact that there are dozens of potential lithium mines in the United States and Canada, most are in various stages of growth and many are years away from manufacturing. This can largely be attributed to environmen tal lawsuits that are delaying development due to various points for litigation in US regulatory law. Many of these mines have to raise billions of dollars in investment with no guarantee that they will produce
RARE EARTH
30 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022
enough lithium to meet North America’s needs. Since mid-2021, the price of lithium has increased fivefold, bringing the cost of electric vehicles to around $66,000, just a few thousand dollars less than the median household income and $20,000 more than the average for all new car sales. And prices continue to rise.
High EV prices are caused by a scarcity of batteries, raw materials like lithium, and components such as semiconductors. When there is strong demand from wealthy buyers who want to own a Tesla or be the first on their street to flaunt a luxurious electric vehi cle, automakers have little incentive to build and sell cheaper EV models. Furthermore, many low- and middle-income individuals do not have garages or driveways and there aren’t enough public charging stations for charging their EVs.
The bottlenecks will take years to remove because automakers and battery and chip suppliers must obtain permits, build new factories, and equip them. Commodity sup pliers must open new mines and construct refineries, which require years of permitting procedures. Despite federal government incentives, charging companies are strug gling to install stations fast enough to meet the demand.
At Silver Peak (Nevada), Albemarle works as the only active lithium mine in the United States. Lithium is extracted from brine, a liquid found beneath the ground. Some Tesla batteries contain lithium from Nevada but the site’s total annual output is enough for about 80,000 vehicles—roughly one-fifth of the EVs purchased in the United States in the first six months of this year (370,000 EVs).
Albemarle also manufactures lithium in Chile and Australia. The company is working to reopen a lithium mine in Kings Mountain (North Carolina) and intends to build a refin ery in the Southeast. However, if other states follow California’s lead and ban internal

combustion engines, these projects will be insufficient to meet the demand.
At the Quebec mine, rock is blasted loose and crushed before being processed in stages to remove waste. A short distance from the mine, inside a large building with corrugated blue metal walls, a laser scanner separates light-colored lithium ore using compressed air jets. The ore is then refined in vats of water and detergent where lithium floats to the surface and is skimmed.
The finished product resembles fine white sand, but it contains only about 6% lithium. The remainder consists of aluminum, silicon, and other substances. The material is then sent to refineries, the majority of which are in China, to be further purified. The separation
procedure employs only recycled water and electricity from Quebec’s hydropower plants.
Raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel must be produced and processed in order to manufacture electric vehicles and renewable technologies. Currently, China – where mining and manufacturing regu lations are less stringent than in the United States – dominates the battery supply chain especially in the processing of these raw materials.
Environmentalists in the United States do not consider mining and processing of these materials to be “green”. Canada is a little more lenient than the US and, as a result, the lith ium mine in Quebec may be able to succeed especially if lithium prices remain high.
China currently dominates the processing of critical metals required by EVs and renewable technologies. Lithium processing also necessitates expertise, which is scarce in the United States and among the country’s allies.
www.skillings.net | 31
The deep sea could be one answer to the shortage of critical materials needed for a transition to low-carbon technologies. However, there are many unknown risks that come with this nascent industry and below I explore some key environmental and social considerations against the context of what is currently understood about deep sea mining.

32 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022
Deep-Sea Mining Environmental and social considerations and risks

By Tom Mills, Founder & Managing Director of Two Oceans Strategy, London, UK. Email:: tom.mills@twooceansstrategy.com Website: www.twooceansstrategy.com

The global demand for meTals and minerals is projected to double or even triple by 2050 and pro duction of battery metals such as graphite, lithium and cobalt will have to increase by nearly 500% to meet the growing demand for clean energy technologies.
Simultaneously, supply to meet this demand from easy to reach terrestrial mineral sources is constrained by declining ore grades, geo-economic instability or ESG risks. This situation makes terrestrial mineral production increasingly difficult and expensive. In fact, ESG risks are the top-ranked risk to mining businesses in 2022, according to EY’s annual survey of mining company leaders.
Against this increasingly challenging backdrop, governments and companies are looking to alternative options to extracting minerals from the land, including the deep-sea and even asteroids. Society, governments, and companies are faced with a tradeoff between meeting mineral demands from increasingly challenging political, social and environmental contexts.
profiles in miningPiM
www.skillings.net | 33
The deep sea could be one answer to the shortage of critical materials needed for a transition to low-carbon technologies. However, there are many unknown risks that come with this nascent industry and below I explore some key environmental and social considerations against the context of what is currently understood about deep sea mining.
Deep Sea Mining: The Commercial Driver
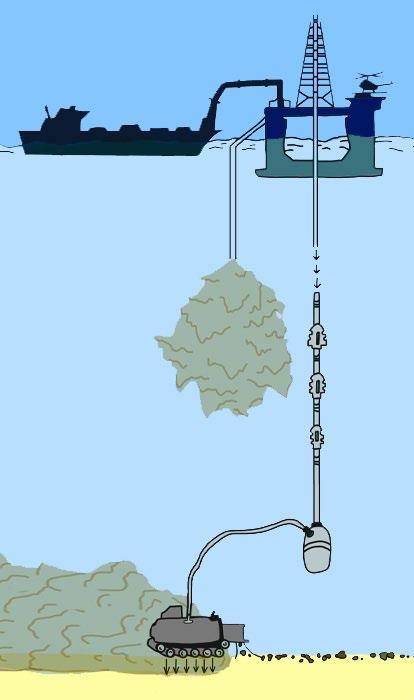
Deep sea mining (DSM) involves the retrieval of minerals and deposits from the ocean floor at depths of 200 meters or greater. There are three main types of mineral resources that can be mined from the deep sea: polymetallic nodules, cobalt rich crust, and polymetallic sulphides or vents. Polymetallic nodules, the best studied of these three types, usually exist unattached on the sea floor and are rocks rich in cobalt, nickel, copper, and manganese.
They are found in the highest intensity in Indo-Pacific Ocean. To date, DSM has been restricted to exploration activities and the earliest estimated start date of commercial production of DSM is late 2024. The metals found on the seabed could be enough to electrify 280 million vehicles according to The Metals company, with claims that DSM will also result in less significant envi ronmental and social impact compared to terrestrial mining. An industry-funded white paper also suggests there will be fewer social impacts and lower lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions than terrestrial mining.
Another obvious driver for DSM is its emerg ing commercial proposition. Industry experts, Sharma, estimates the commercial value of polymetallic nodules in a 75,000 sq km seabed area at USD$21bn, for an investment cost of $14bn over a 20-year period. Pri vate enterprises and states alike would be expected to share profits of such an enter prise, whether by sale or by taxes, royalties, levies, or other financial mechanisms.

34 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022 PROFILES IN MINING
Environmental considerations: The great unknown
Despite the surface level appeal of deep-sea mining and obviously lucrative potential of the industry, risks to the environment and people are not well defined. Within academic literature, there are research indicating the fragility of deep-sea ecosystems, their slowness to recover from disturbance, and the paucity of data informing understanding of the seafloor is abundant.
Even where progress has been made with environmental research, thorough analyses will be needed on environmental impacts specific to any contract area. As it stands, there are known areas of ecological or bio logical significance in the Central Indian Ocean Basin and the Clarion Clipperton Zone. Dr. A Kung also encourages states and DSM companies to consider the wider environmental impacts for example, the impacts of onshore processing, including waste rock generation and disposal.
The impact of deep-sea mining, in terms of the planet’s biological systems, the sea bed’s role as a carbon sink and the potential opportunities for new biomedical develop ments from species in the deep is almost entirely unknown and unresearched. At the same time Deep Sea Mining has become an extremely contentious issue, with several of the world’s largest companies and gov ernments issuing moratoriums on minerals mined from the deep sea. This may have a bifurcating impact, splitting supply chains that accept deep sea mined minerals and those that do not.
On solution put forward by the International Seabed Authority, the governing body for deep sea mining in international waters, is the use of an Environmental Impact Assess ment (EIA). However, EIA rests on the logic that environmental impacts can be predicted and assessed, where for DSM uncertainties such as the ongoing development of tech nologies and lack of projects that serve as a
precedent present challenge to this method. This is not the only issue at play; other uncer tainties to consider are the complex nature of seafloor sites, which could mean a sample may not represent the whole site accurately. The slow-changing, fragile nature of seafloor ecosystems also make it likely that any harm will take substantial time to naturally repair.
Social Considerations: The issue of measuring indirect risk
Some direct social impacts that come to mind when considering deep sea mining are risks of physical disturbances to land, coastlines, and infrastructure. This could be caused by processing facilities, waste disposal, increased shipping requirements. Further, depending on the project there might be competing uses of land and water amongst marine parks and recreational areas, shipping zones, fisheries, subsea telecommunication infrastructure, and ports.
The impacts deep sea mining will have on fish, water and air quality and noise, will also have consequential effects on people. Assess ing these direct, physical activities risks to people is relatively straightforward. By con trast, indirect social risks are currently being debated and have not yet been resolved. Two particular social impacts are free, prior, and informed consent (FPIC) and economic extension of the idea of acceptance:
FPIC originates in Indigenous Peoples’ rights, and stems from the recognition that govern ments and private parties should obtain the free, prior, and informed consent of Indig enous people when seeking to undertake a project on Indigenous land. Neither FPIC nor a social licence to operate have a formal approval process. Anthony Kung et al prelude to in the 2021 research paper - Governing deep sea mining in the face of uncertaintyeven within terrestrial mining it is unclear as to how either can be obtained, maintained, or proven. For instance, we have to ask the question: who constitutes the host commu
Deep sea mining (DSM) involves the retrieval of minerals and deposits from the ocean floor at depths of 200 meters or greater. There are three main types of mineral resources that can be mined from the deep sea: polymetallic nodules, cobalt rich crust, and polymetallic sulphides or vents.
www.skillings.net | 35 profiles in miningPiM
My concern with DSM, is there is no such connection as no one lives on the seafloor. Yet, deep cultural connections to the ocean are prevalent across the globe and figuring out the correct way to weigh in these connections will be vital. Secondly, multinational companies – including BMW, Volkswagen, Renault, Google, Samsung– have declared a moratorium on using DSM metals in their products.
nity? Other than those with formal power, such as landowners themselves, who may effectively veto a project by withholding consent? How is many people’s withhold ing required for a government regulator to decline to approve it?
These answers are not yet solved and will need to be on a project-by-project basis for communities to be protected and social rights to be properly administered. For terrestrial mining, connection to land is the basis for FPIC and social licence.
My concern with DSM, is there is no such connection as no one lives on the seafloor. Yet, deep cultural connections to the ocean are prevalent across the globe and figuring out the correct way to weigh in these con
nections will be vital. Secondly, multinational companies – including BMW, Volkswagen, Renault, Google, Samsung– have declared a moratorium on using DSM metals in their products.
The World Economic Forum has also started a deep-sea mining ‘dialogue’ platform to discuss the extension of responsible sourcing standards to DSM. These developments raise questions for deep sea miners as to whether the metals will have a beneficial place for real-world use and perform to accelerate a green transition, as was originally hoped.

Considering the potential demand for the resources that will power the green transi tion and the lucrative character of deep-sea resources that have been understood to
exist, pressure to accelerate commercial mining projects is unsurprising. While some experts say we must mine the deep sea to combat climate change, I would argue that as it stands, we know too little about the potential damage to the environment to read ily consider mass-commercial expeditions. However, I do not think the industry should be pushed aside or coined as evil.
The strength of the governance regime and how it is administered will ultimately be the determining factor of whether the liberation of resources from the seabed positively or negatively contribute to the common heri tage of mankind. The International Seabed Authority has the weight of the world’s oceans on its shoulders.
36 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022
Mineral Management Software Suite
enerTel formed a sTraTegic parTnership WiTh haymaker min erals & Royalties III, LLC ("Haymaker") in October. This partnership serves as guidance for Enertel in the creation of their recently released mineral management platform.

The collaboration started during the development and release of Enertel's QuantumCast: Minerals, a comprehensive platform for managing mineral portfolios that integrates the best elements of financial modeling, mineral management, and reservoir appraisal.
CEO OF ENERTEL, FRED ENOCHS, SAID,
"For many years, Enertel has developed customised data management systems for the energy industry. Since mineral managers are constantly seeking for methods to improve efficiency and because there aren't many reliable solutions on the market to address many of the current pain issues, we find the mining sector to be particularly appealing. We have the on-the-ground knowledge we need to address these issues because to Haymaker's experience managing tens of thousands of wells on behalf of institutional investors."
HAYMAKER'S MANAGING PARTNER, KARL BRENSIKE, SAID,
"Since we've been operating in the mineral market since 2004, there haven't really been any third-party software options. When we first launched Haymaker, we made the decision to develop our own proprietary systems and handle everything internally, which required additional personnel and costs. These high demands forced us to
look for a totally outsourced solution for Haymaker III that could handle things more effectively, more quickly, and with ongoing innovation. We believe that Enertel is the market leader, thus it was a wise choice to partner with them and work together to improve their platform."
ABOUT ENERTEL
Founded in 2018 by oil and gas industry veterans and former CIA clandestine officers, Enertel is a data and analytics firm that blends oil and gas analytics with US intelligence best practices. They provide strategic advisory services and configurable, full-suite platforms that combine engineering rigor and financial management workflows for clients across the E&P, midstream, minerals, OFS, private equity, hedge funds and banking sectors. visit www.enerteladvisors.com.
ABOUT HAYMAKER MINERALS & ROYALTIES
Haymaker was founded in 2013 and has used various entities to manage and acquire mineral and royalty interests in over 35,000 oil and gas wells across the United States. visit www.haymakermineralsandroyalties.com.
www.skillings.net | 37
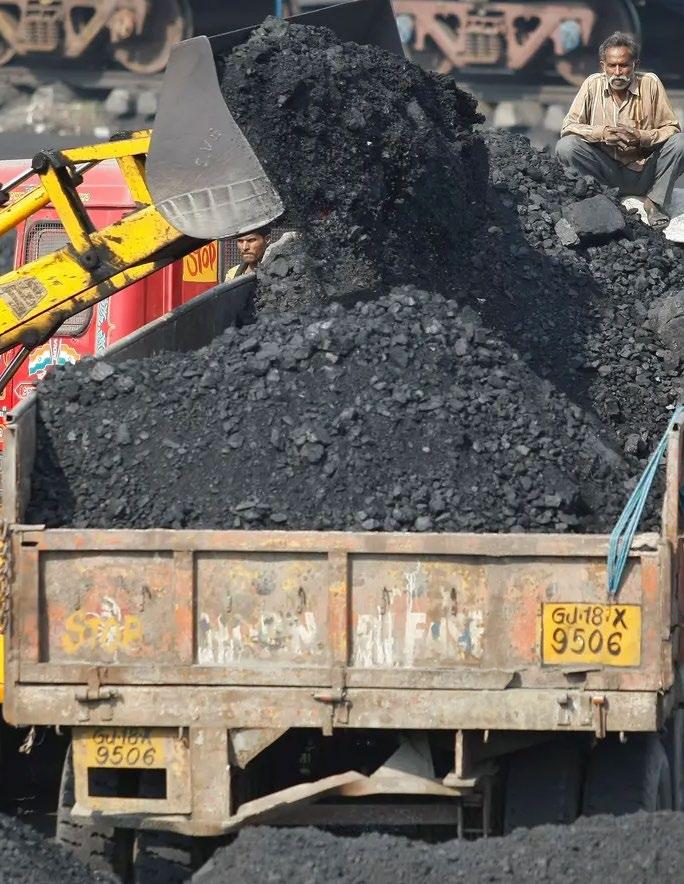

COAL COMPANIES RECKLESSLY GOING GO! 38 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022 SPECIAL FOCUS
Despite this, research in October 2022 from German NGO Urgewald and 40 partner organizations shows that roughly 500 coal businesses are still considering building new mines or power stations.

Director of Urgewald, Heffa Schuecking, stated in a news statement introducing the new statistics that "out of the 1,064 enter prises in our database, 490 are planning new coal power stations, new coal mines, or new coal transportation infrastructure."
Amid a climate emergency, pursuing new coal plants is foolish and irresponsible. These coal developers should be immediately removed from the portfolios of investors, banks, and insurance.
The updated Global Coal Exit List (GCEL), an initiative of Urgewald and its partner NGOs, claims to be "the most complete public database on the coal sector" and includes the new information as part of its 2022 update. It monitors more than 1,800 subsidiaries and more than 1,000 enterprises that are involved in the value chain of thermal coal.
According to the update, 46% of coal com panies were still growing. Production of coal could rise by 37% as a result of new mining initiatives. A further 476 gigawatts of coal-powered capacity are also under construction, which would represent a 23 percent increase in capacity.
All of this occurs despite the fact that world leaders decided to "accelerate efforts towards the phasedown of unabated coal" at the conclusion of the COP26 climate conference
in Glasgow last year in 2021. However, past responses to climate agreements are con sistent with this lack of progress.
According to Schuecking, the combined capacity of the coal fleets of Germany, Russia, Japan, and Poland has expanded by about 157 gigawatts since the Paris accord was signed in 2015.
Of all the fossil fuels, coal emits the most carbon. According to the GCEL, a 2018 assessment from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) found that
by 2030, coal use for energy must decrease by 78% to achieve the 1.5 degree Celsius objective. The IEA further stated that indus trialized countries needed to retire their coal plants by 2030, and developing countries needed to do so by 2040 in order to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050, according to the press release. However, relatively few businesses are actually pur suing these goals.
The news announcement quoted Schuecking as saying, "While the warnings published by IPCC and UNEP become more and more
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), if the world is to keep global warming to the Paris Agreement's target of 1.5 degrees Celsius over pre-industrial levels, no new fossil fuel infrastructure, including coal mines and plants, may be developed beyond 2021.
A
coal mine in
China. zhou shu
/ Moment / Getty Images www.skillings.net | 39
grave from one UN Climate Summit to the next, our data regarding firms' transition plans remain depressingly consistent."
"The overwhelming majority of corporations on the GCEL continue to have no plans to retire the coal assets, which are hastening the collapse of our climate systems. Clear and imminent coal exit dates are necessary for a real transformation.” Only 56 businesses, or 5.3% of the total, had announced a coal leave date, and most of those dates were much too late to fulfill climate commitments, according to the update. There was a catch: only 27 enterprises, or 2.5 percent, had announced withdrawal dates that were consistent with global objectives.
The majority of these 27 corporations are just preparing to convert their coal facilities to gas or to sell them rather than to retire them, Schuecking said of his analysis of their transition plans. "In the end, we only found 5 enterprises with coal transition strategies that might be regarded as linked with Paris."
As per reports, the majority of the new mining operations being proposed are in China, India, Australia, Russia, and South Africa. Although Coal India was the largest mine developer in the world, the update discovered that China had the newest coal mining projects scheduled.
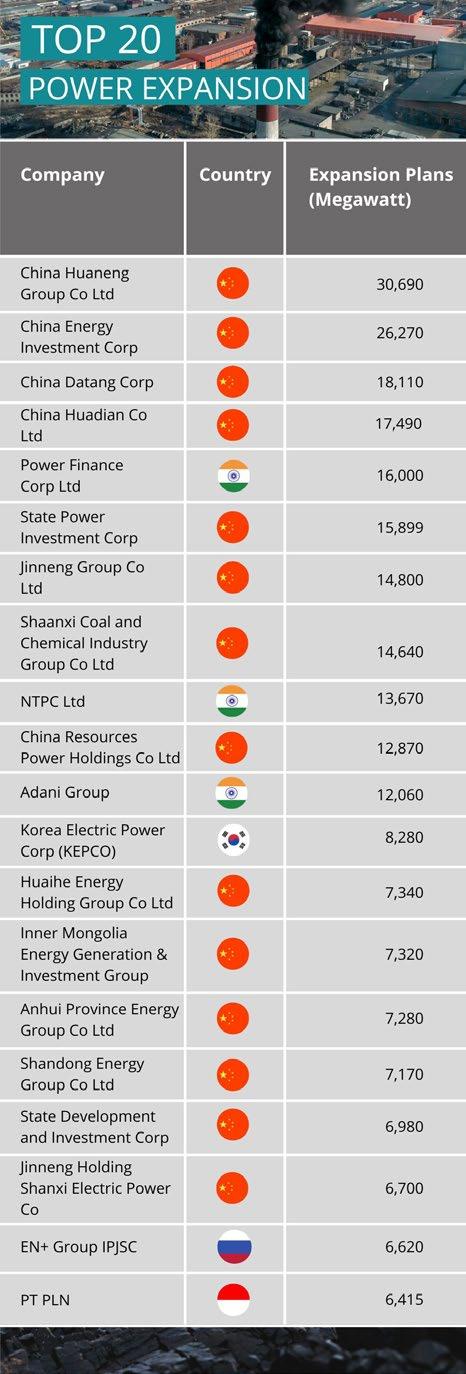
China also had the newest coal plants planned, accounting for 61 percent of the total new capacity under construction. Addition ally, all four of the corporations that planned to build the most new plants were Chinese.
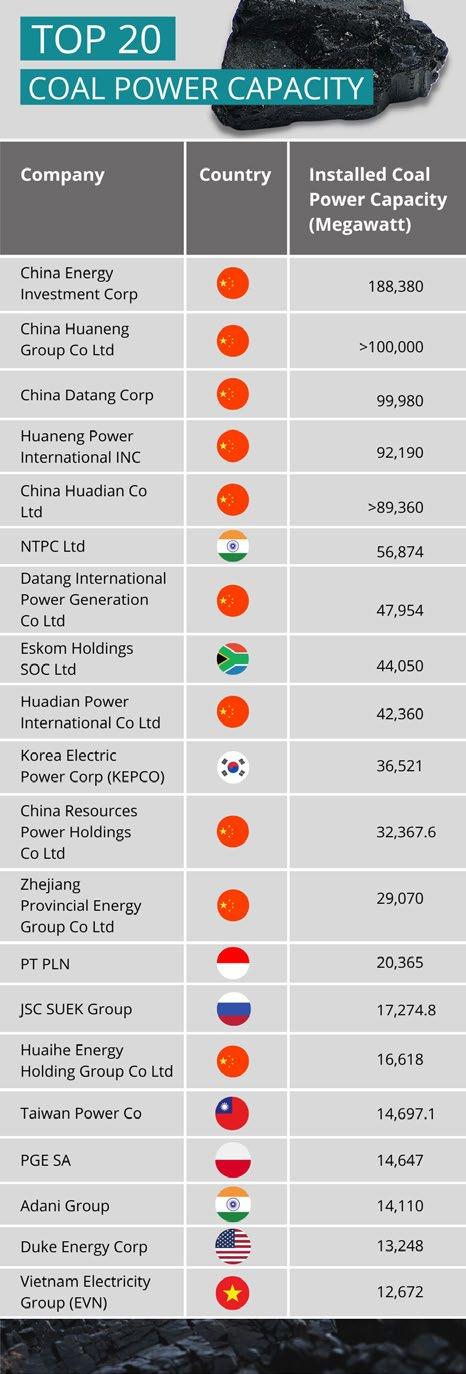
According to a press release from the Asian Peoples' Movement on Debt and Develop ment, Lidy Nacpil, coordinator, "the world welcomed President Xi Jinping's 2021 announcement that China would stop building new coal power plants abroad, but China needs to adopt similar measures for its domestic energy system if it wants to become an actor for a 1.5°C world."
With only 13 gigawatts of officially aban doned coal plants as of yet, the prohibition on coal plants in other countries has also been badly enforced.
The United States was not exempt, however, as it has the third-largest fleet of coal plants
in the world, with a combined capacity of around 218 gigawatts. Additionally, it has not established a national coal-power phaseout date and only decommissioned 8.4 gigawatts of capacity as of 2021, lagging behind nations like Italy, France, and the UK.
SPECIAL FOCUS
40 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022
CGG Awarded Critical mineral exploration Study in Argentina
cgg ’ s m inerals & m ining team has been awarded a con tract by DLE Resources to assess the regional potential for lithium and potash mineral exploration in Argentina.
CGG’s Minerals & Mining team has been awarded a contract by DLE Resources to assess the regional potential for lithium and potash mineral exploration in Argentina. South America hosts some of the world’s largest deposits of these vital commodities, and recent developments and discoveries in Argentina make this an exciting region for frontier mineral exploration. The awarded screening study will provide vital intelligence to identify and assess opportunities for future development.
CGG’s specialist mineral exploration geolo gists will source, compile, and interpret data from a wide range of sources in preparation for a prospective ranking.
DAVE PRIESTLEY, VP, ENERGY TRANSITION & ENVIRONMENT, CGG, SAID:
“This award is the latest in a series of mineral exploration projects conducted by our fast-growing Minerals & Mining team. It is testament to the capabilities and experience that CGG brings to frontier mineral exploration activities, with a particular focus on combining expertise, technology and data-driven solutions to generate new insights. This assessment of mineral prospectivity in Argentina will support the industry search for these critical minerals and is another example of CGG’s commitment to enable responsible and sustainable exploration in the mining sector.”
Slam Exploration Mobilizing to Drill Gold Veins at Menneval
slam exploraTion lTd. (“slam” or The “company” on Tsxv: SXL) is pleased to announce it is mobilizing a diamond drilling rig a drilling program on its wholly-owned Menneval gold project located in the mineral-rich province of New Brunswick, Canada. The rig is to be transported over the weekend, with drilling expect to start on or about Monday, September 19, 2022.
The slam exploration intends to drill up to 1,000 metres in approximately 10 holes to test 2 gold zones discovered by SLAM in 2020-2021. This includes up to 6 holes on Zone 18. These holes are planned to test for extensions beneath core intervals grading up to 162.5 g/t gold over 0.2 m and 56.50 g/t gold over 0.51 m associated with visible gold in holes reported by the Company on December 03, 2020, and January 20, 2021. Previously, the Company had announced multiple sites of visible gold with assays up to 3,955 g/t gold over 0.10 m thick from trench samples reported on December 03, 2020.
SLAM exploration intends to drill 4 holes on Zone 22, where the Company reported drilled core intervals grading up to 5.40 g/t gold over 0.2 m on December 03, 2020. Each of the Zone 22 holes will test multiple quartz veins that are part of a series of gold-bearing veins trending north-easterly over a strike length of 1,400 m. The Zone 22 veins are associated with a soil anomaly ranging from 5 to 206 ppb (0.206 g/t) gold that stretches 2,800 metres eastward from vein No. 18. For additional information and maps, please visit the following page on the Company’s website: Menneval Gold Project or call Mike Taylor 506-623-8960.
$30,000 NBJMAP Grant:
The Menneval drilling program will be supported in part by a grant of $30,000 under the New Brunswick Junior Mining Assistance Program (“NBJMAP”). The Company wishes to thank the Province for its continued recognition of the Menneval project and its importance to the emerging gold industry in New Brunswick.
The Menneval Project:
The Company drilled 20 holes in the 2021 exploration program and intersected multiple gold veins discovered in 2020-2021 on its flagship Menneval Gold project. The property is comprised of 351 mineral claim units covering 7589 hectares located in northwestern New Brunswick.
The Company holds a 100% interest in these claims with the exception of 4 claim units covering 105 hectares that are subject to a 1.5% NSR. The Company can buy down 0.5% of the NSR for $500,000 and it has the right of first refusal on the remaining 1% NSR.
www.skillings.net | 41
According to John Russell, the managing director of FOGMAKER South Africa, "Based on our past experience, this mining exhibition serves as an excellent meeting point for all our stakeholders, from customers, end-users, and industry experts to our original-equipment manufacturer (OEM) partners." This year's show will also mark the introduction of Q-TEC Fire's foam fire suppression solution into the company's product line.


Russell emphasizes the need to take action to reduce the fire risk through design and operational procedures because fires pose a real and serious threat to mining operations, particularly because every diesel engine-op erated vehicle and machine is susceptible due to the presence of heat, rapid airflow, and flammable fluids.
A small fire in a mine can spread quickly, causing catastrophic results, including loss of life and exorbitant costs associated with damages and downtime. If the fire risk is still unacceptable, it is essential to make sure that there is an efficient, certified, and reliable fire suppression system in place.
“Visitors to our display P17 in Nasrec's lake area may once again look forward to wit nessing this very successful technology in action”, Russell says. "Building on the amazing success of the live demonstrations of our FOGMAKER triple-action fire-suppression system at the 2018 show," he adds.
The daily live demos will be carried out on a FOGMAKER system mounted on an OEM mining machine, demonstrating both the potential of water-mist technology to completely flood an area as well as our abil ity to integrate our technologies into OEM equipment to ensure safe operation.
Stakeholders will be able to interact with a sizable delegation from FOGMAKER Inter national as they travel to the exhibition from Sweden
take part in discussions about

SPECIAL FOCUS
and
fogmaker south africa: dominate ema 2022 show: With Smart, Efficient And Cost-Effective Fire-Suppression Practices fogmaker souTh africa, a supplier of high pressure WaTer mist fire suppression systems, will use Electra Mining Africa 2022 as a showcase for its well-known fire suppression systems as well as to unveil fresh goods and innovations for the mining sector. 42 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022
FOGMAKER's international operations. According to Russell, "We are also very happy to announce that we will be showcasing real FOGMAKER installations on a variety of OEM equipment on partner OEM displays.
Product Data
The lightweight, low-maintenance FOGMAKER system effectively puts out the fire in a matter of seconds by using the power of the purest extinguishant—water—in the form of a high-pressure mist.
The system uses water and 3% Aqueous Film Forming Foam (AFFF) to quickly target the heat, oxygen, and fuel elements of a fire. Rus sell continues, "We call this the FOGMAKER TRIPLE ACTION3 effect. The FOGMAKER system is intelligently developed to be compact and be installed in any direction, making it suitable for any application where diesel-powered machines are being run.
As is the case with the majority of mobile mining equipment, this makes it particu larly appropriate for machines with limited mounting space for storage cylinders. In order to fulfill international fire suppres sion standards, FOGMAKER systems are produced in accordance with ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 standards, and they have received certification from internationally renowned organizations.
He adds, "With the addition of the Q-TEC Fire Services foam fire suppression system to our product line, we recently expanded our reach for solutions into very large mobile equipment and stationary plant.”

With a strong 30-year history of offer ing foam fire suppression systems made in Australia, Q-TEC is an Australian firm. Q-TEC provides the "most cutting-edge and designed foam-spray fire suppression systems to the mining industry" and uses the F3 Fluorine Free Foam Agent, which complies with all US Environmental Pro tection Agency requirements.” The method,
according to Russell, is excellent for bigger mobile mining machinery as well as sta tionary apparatus like conveyor belts and diesel bowsers.
The military, maritime, ports, airports, bus & coach, and forestry industries can all benefit from the FOGMAKER and Q-TEC fire suppression systems. In order to facil itate the protection of large fleets, where the upfront costs are typically prohibitive, Russell continues, "Our service offers rentown financing options.
Russell adds that although the company's fire suppression systems are successful, which is supported by extensive global certification, it is ultimately the design, installation, and maintenance of the system that determines the effectiveness of any fire suppression system when it is activated.
In turn, he argues, this depends on the competence and education of the installa tion professionals, and the business takes pleasure in its "very competent and profes sional team." The low total cost of ownership is another added benefit provided by the
FOGMAKER and Q-TEC solutions, which is a result of the machines' long lifespans, minimal maintenance requirements, and availability.
Additionally, by assuring that the machine cannot operate without an active fire suppression system, Russell adds, "our tech nologies' ability to easily connect with OEM and third party systems promotes safety."
All Electra Mining attendees are cordially invited to stop by our booth to view these systems in action and to speak with our knowledgeable team members, who are glad to answer any questions they may have regarding our offerings. We anticipate a very successful performance and are excited to provide live entertainment for everyone at our notorious Thursday night event," he adds.
With its sibling firms Integrated Air Solutions, Integrated Pump Technology, Integrated Pump Rental, and Sunward Africa, FOG MAKER South Africa, a proud subsidiary of GiGi Investments, will exhibit at Elec tra Mining.
FOGMAKER South Africa Stand P17 www.skillings.net | 43
Is It Possible For The Iron Ore Mining Industry To Go Green?
WiTh The passage of Time, The World is finally undersTanding and taking climate change seriously. It is certain that the mining industry leaves a significant carbon footprint. According to The World Counts, the mining of iron core produces a large amount of air pollution in the form of nitrous oxide, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and sulfur dioxide from diesel generators, trucks, and other mining equipment.
The company is planning to phase out fossil fuels and replace them with carbon-free fuel sources, such as hydrogen, that can still power heavy machinery. Alongside, Fortescue has also announced that they will be deploying two to three gigawatts (GW) of renewable energy and battery storage across all of their mining sites.

“Consistent with Fortescue’s disciplined approach to capital allocation, this investment in renewable energy and decarbonisation is expected to generate attractive economic returns for our shareholders through energy cost savings and a sharp reduction in carbon offset purchases, together with a lower risk cost profile and improvement in the integrity of our assets,” said Dr. Forrest.
He is also encouraging other mining com panies to make the big switch for the betterment of the environment and for the sake of future generations. The excessive amounts of carbon being produced by the industry is very harmful to the ozone layer and can also intensify the effects of cli mate change.
Green Power Generators
Mining operations can also lead to water pollution since the acid that comes from mines can sometimes flow directly to nearby bodies of water. On a positive note, many mining companies are now trying to make the big shift to green energy.
Fortescue Metals Group is one of the world’s largest iron ore producers. They have recently announced a 6 billion USD plan to switch to renewable energy by 2030. The company aims to eliminate fossil fuel usage
in mining operations and to achieve net zero emissions by 2030.
“Fortescue Metals group has proven you have an alternative and it is a good commercial, solid alternative… You can make money and you can stop cooking our planet. I am saying to every heavy industry company, every heavy manufacturing company, take the first step” Fortescue Chairman, Dr. Andrew Forrest stated.
Researchers are currently studying decommissioned mines to determine if they can be transformed into energy storage facilities. According to Keweenaw Energy Transition Lab at Michigan Technological University or MTU, a group of researchers are looking into opportunities and barriers for repurposing a decommissioned mine into a pumped underground storage hydropower or PUSH facility.
Researchers have found that the PUSH system can be profitable and can be used
44 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022 SURFACE MINING
for a long period of time to store energy and generate it as well. These transformed mines have a positive impact on the environment and economy apart from having significant societal implications. Currently, over 1,000 sites in 15 states are being studied to deter mine if they are suitable for the PUSH system.
Roman Sidortsov, an MTU professor, and Timothy Scarlett, an industrial archaeol ogist, are looking at mines located in the Keweenaw Peninsula. They are positive that these are suitable for the PUSH system
taking into account its technical, economic, legal, regulatory, water quality, social, and community engagement issues.
“Everything estimated is based on the existing technology, the existing structures—virtually no new work in terms of rebuilding the mine or additional blasting. The team was also cautious about revenue predictions. For example, they estimated revenue from only buying and selling electricity on the market but noted that there are other services that could be money-making endeavors. These
include the ability to “black start” the energy grid after a power failure. If the energy grid is underpowered or there are significant blackouts, PUSH can come to the rescue,” said Sidortsov.
ADVERTISING INDEX
ABT
Barr Engineering


CR
FloLevel
Fryberger.......................................
We thrive on challenges
General Equipment

Global Minerals

Golder
Halcor
Lake Superior
Malton Electric

ME Elecmetal
Minnesota Power
Mielke Electric
Naylor
Neo
Northern Engine
Optiro
Azcon 45
21
15
Meyer 23
Technologies ................. 25
15
Supplies ....... 05
Engineering ....... 45
Associates ........................ 45
........................................... 13
Chapter ISEE ......... 45
Company ............ 45
............................... 07
......................... 17
Works .................. 17
Pipe ................................... 48
Solutions ............................... 19
& Supply ............ 45
............................................ 02 SEH ............................................... 21
golder.com
www.skillings.net | 45
august 2022 crude steel production
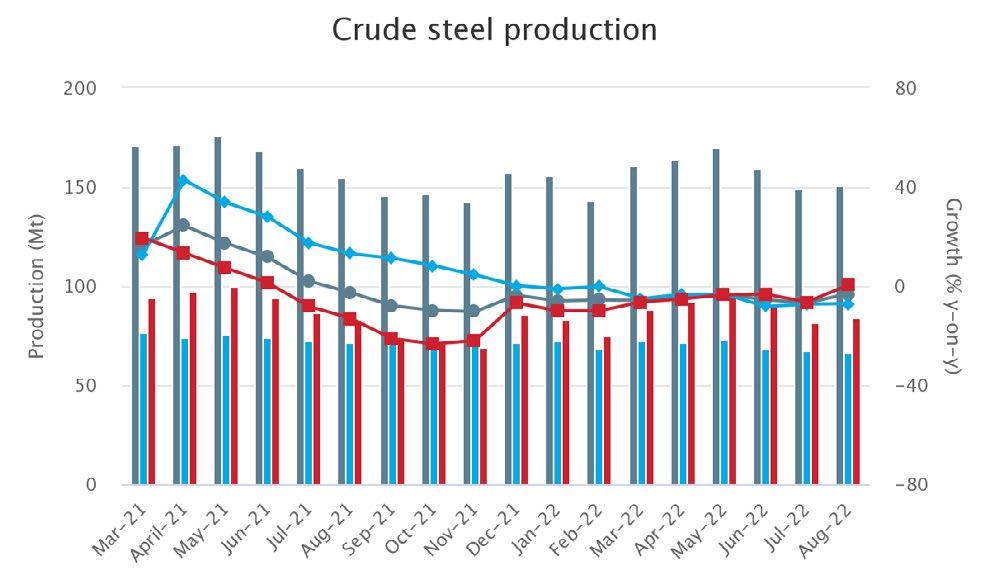
Worldcrude steel production for the 64 countries reporting to the World Steel Association (worldsteel) was 150.6 million tonnes (Mt) in August 2022, a 3.0% decrease compared to August 2021.
CRUDE STEEL PRODUCTION BY REGION
Africa produced 1.3 Mt in August 2022, up 3.5% on August 2022. Asia and Oceania produced 112.6 Mt, down 0.2%. The EU (27) produced 9.7 Mt, down 13.3%. Europe, Other produced 3.6 Mt, down 18.6%. The Middle East produced 3.2 Mt, up 34.2%. North America produced 9.6 Mt, down 5.4%. Russia & other CIS + Ukraine produced 6.9 Mt, down 22.4%. South America produced 3.6 Mt, down 10.1%. The 64 countries included in this table accounted for approximately 98% of total world crude steel production in 2021. Regions covered by the table: Africa, Asia and Oceania, European Union (27), Europe, Middle East, North America, Russia & other CIS + Ukraine, South America.
Table 1. Crude steel production by region
TOP 10 STEEL-PRODUCING COUNTRIES
China produced 83.9 Mt in August 2022, up 0.5% on August 2021. India produced 10.2 Mt, up 1.2%. Japan produced 7.3 Mt, down 7.4%. The United States produced 7.0 Mt, down 7.1%. Russia is estimated to have
produced 5.9 Mt, down 5.5%. South Korea is estimated to have produced 6.1 Mt, down 0.4%. Germany produced 2.9 Mt, down 2.3%. Türkiye produced 2.8 Mt, down 21.0%. Brazil produced 2.8 Mt, down 11.3%. Iran produced 2.1 Mt, up 64.7%.
Table 2. Top 10 steel-producing countries
2022 (mt) % change aug 22/21 jan-aug 2021 (mt) % change jan-aug 22/22 africa 1.3 3.5 9.7 -7.4 asia and oceania 112.6 -0.2 925.1 -4.3 eu (27) 9.7 -13.3 95.3 -6.9 europe, other 3.6 -18.6 31.0 -8.4 middle east 3.2 34.2 28.5 6.9 north america 9.6 -5.4 76.0 -3.6 russia & cis + ukraine 6.9 -22.4 59.1 -18.2 south america 3.6 -10.1 29.2 -4.1 total 64 countries 150.6 -3.0 1,253.9 -5.1
aug 2022 (mt) % change aug 22/21 jan-aug 22 (mt) % change jan-aug 22/21 china 83.9 0.5 693.2 -5.7 india 10.2 1.2 83.5 7.1 japan 7.3 -7.4 60.7 -5.2 united states 7.0 -7.1 54.9 -3.7 russia e 5.9 -5.5 48.9 -5.8 south korea e 6.1 -0.4 46.0 -3.0 germany 2.9 -2.3 25.4 -4.8 turkey 2.8 -21.0 24.4 -8.8 brazil 2.8 -11.3 23.1 -4.5 iran 2.1 64.7 19.5 7.8
The 64 countries included in this table accounted for approximately 98% of total world crude steel production in 2020. Regions and countries covered by the table: Africa: Egypt, Libya, South Africa. Asia and Oceania: Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Pakistan, South Korea, Taiwan (China), Vietnam. CIS: Belarus, Kazakhstan, Moldova, Russia, Ukraine, Uzbekistan. European Union (27). Europe, Other: Bosnia-Herzegovina, Macedonia, Norway, Serbia, Turkey, United Kingdom. Middle East: Iran, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates. North America: Canada, Cuba, El Salvador, Guatemala, Mexico, United States. South America: Argentina, Brazil, Chile,
STATISTICS
Colombia, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru, Uruguay, Venezuela
aug
46 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW November 2022
521
43 -6.3
-10.2
-14.3
-32.0
Kingdom
E.U.
97
540 521 3.6
680
642
34
891 765
376 8.9
550
642
70
596 -19.8
-10.0
513 -14.5
-12.9
886 -11.0
054 -9.1
890 -11.9
-8.5
934 -19.5
409 -6.6
185 -0.5
180 -12.1
477 -21.5 Paraguay 3 e 3 -4.4 22 -17.5 Peru 105 e 91 15.8 671 -45.4 Uruguay 5 e 5 -7.2 47 -24.6 Venezuela 2 e 0 315.8 29 -43.6 South America 3 654 3 143 16.3 38 158 -8.4 Egypt 994 574 73.0 8 229 13.4 Libya 73 63 16.2 495 -18.4 South Africa 292 e 297 -1.5 3 877 -37.0 Africa 1 359 934 45.5 12 600 -10.1 Iran
660 e 2 224 19.6 29 030 13.4 Qatar 85 186 -54.3 1 218 -52.4 Saudi Arabia
664 -33.8 7 775 -5.1 United Arab Emirates 280 297 -5.8 2 722 -18.2 Middle East
465 3 371 2.8 40 745 2.7 China
052 999 5.2 India
252 84 692 7.7
796 9 383 4.4 99 570 -10.6 Japan
526 7 785 -3.3 83 194 -16.2 South Korea
952 5 880 1.2 67 121 -6.0 Pakistan
e 261 45.6 3 743 13.3 Taiwan, China
700 e 1 693 0.4 20 570 -6.3 Thailand
14.8
420 4.1 Vietnam
600
876
500 11.6 Asia
117 1.6 Australia
490 0.0 New Zealand
076 -1.4
3.8 586 -12.2 Oceania
COUNTRY DEC 2020 DEC 2019 %CHANGE DEC-20/19 2020 % CHANGE Austria 530 e
1.7 6 665
Belgium 359 505 -28.9 6 119 -21.1 Bulgaria 40 e
485
Croatia 15 e 7 101.9 47
Czech Republic 408 359 13.7 4 465 0.6 Finland 339 186 81.8 3 500 0.8 France 1 155 918 25.7 11
Germany 3 137 2 835 10.6 35 658
Greece 110 e 94 17.0 1 430 5.9 Hungary 90 164 -44.8 1
Italy 1 500 e 1 404 6.9 20 200
Luxembourg 113
17.3 1
Netherlands
6
Poland
e
5.9 7
Slovenia 50 e
45.0 570
Spain
16.4 10
Sweden 410
4
United
710 e
29.0 7
Other
(28) (e) 680 e
6.0 8
European Union (28) 11 757 10 665 10.2 138 786 -11.8 Bosnia-Herzegovina 75
6.5 759 -5.2 Macedonia 33 24 35.9 180 -24.8 Norway 41 40 3.2 624 0.5 Serbia 119 158 -24.8 1 456 -24.6 Turkey 3 403 2 893 17.7 35 763 6.0 Other Europe 3 671 3 185 15.3 38 782 3.9 Byelorussia 200 e 225 -11.2 2 490 -5.0 Kazakhstan 355 e 374 -5.0 3 835 -7.2 Moldova 45 e 35 28.2 465 18.7 Russia 6 110 e 6 159 -0.8 73 400 2.6 Ukraine 1 906 1 561 22.1 20 616 -1.1 Uzbekistan 80 e 84 -4.8 950 42.6 C.I.S. (6) 8 696 8 438 3.1 101 756 1.5 Canada 1 070 e 1 092 -2.0 11 078 -14.1 Cuba 20 e 22 -8.5 181 -21.4 El Salvador 8 e 8 -5.7 79 -22.5 Guatemala 25 e 26 -3.9 237 -22.6 COUNTRY DEC 2020 DEC 2019 %CHANGE DEC-20/19 2020 % CHANGE Mexico 1 550 e 1 361 13.9 16 854 -8.3 United States 6 434 7 292 -11.8 72 690 -17.2 North America 9 107 9 801 -7.1 101 119 -15.5 Argentina 388 326 19.0 3 651 -21.4 Brazil 2 886 2 462 17.2 30 971 -4.9 Chile 105 e 109 -3.5 1 165 2.8 Colombia 110 e 97 13.5 1 126 -15.5 Ecuador 50 e 50 0.5
2
440
3
91
1
9
7
5
380
1
410 e 357
4
1
e 1
… 19
118 616 111927 6.0 1 351
473 449 5.4 5
59 57
533 506 5.2 6
Total 64 countries (1) 160 858 151 969 5.8 1 829 140 -0.9 (1) - HADEED only. (2) - the 64 countries included in this table accounted for approximately 99% of total world crude steel production in 2019. e - estimated CRUDE STEEL PRODUCTION DECEMBER 2020. Source – World Steel Association www.skillings.net | 47


Name Company Address .........................................................Suite... City:..............................State:..........................Zip:.............................. Phone ............................. Fax .............................................................. E-Mail MINING INFO YOU DON’T HAVE TO DIG FOR... SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW. P.O. 1203 NOKOMIS, FLORIDA 34274 Subscription Information TEL: 888-444-7854 X 4 | FX: 888 261 6014 subscriptions@skillings.net SUBSCRIBE NOW FOR IRON ORE MINING NEWS AND MORE... Check your choice of Subscription Skillings Mining Review Print Subscriptions United Stages Mainland a Print Monthly Magazine Skillings Mining Review - Mail Delivered a Digital Subscription One-Month c $72 12 Months c $800 Skillings Mining Review Print Subscriptions Global a Print Monthly Magazine Skillings Mining ReviewMail Delivered a Digital Subscription One-Month c $250 12 Months c $2950 Skillings NewsRoom Digital Subscription a 3x Weekly Digital Newsletters: The Americas, Global and Equipment a Video News Updates a Digital Monthly Magazine Skillings Mining Review e-mailed a Website Full Access Skillings.net Podcast | Videos One-Month c $4.95 12 Months c $55.00 12 Months c $660.95* *Group License (Unlimited Access Company wide) c Amount Enclosed c Please Bill Me Card Number: Exp. Date: c Visa c Master Card c American Express CVS No. (Security Code):













































 "Sandvik's state-of-the-art battery system facility in Camarillo, California, boasts 100 MWh of annual battery production capacity, as well as acting as a
"Sandvik's state-of-the-art battery system facility in Camarillo, California, boasts 100 MWh of annual battery production capacity, as well as acting as a




























































