Mining Automation The Path To Sustainability

2022 DECEMBER IN REVIEW 111/12 us steel iron ore could bring new boom 18 implementing esg during a recession 28 2022 annual index of skillings mining review 40 07 continuous improvements
in terms of technology and machinery are needed to ensure that the competitive demand of metals is met in a safe manner.
Biden Says Coal Plants ‘Across America’ Will Be Shut Down
2 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022 BIG RESULTS SMALL TEAM Optiro is a resource consulting and advisory group. Our 5 core services are Geology, Mining Engineering, Corporate, Training and Software. In eleven years, our team has travelled the world providing expertise to improve, value, estimate and audit the world’s minerals. Pound for pound we think you’ll find no-one delivers greater value –and BIG results. +$15 BILLION DEALS/ VALUATIONS >780 MILLION oz Au RESOURCE AUDITS >64 MILLION oz Au RESOURCE ESTIMATES >3,000 CLIENTS +2,000 PEOPLE TRAINED 24 COMMODITIES 53 COUNTRIES >4,300 MILLION lb NICKEL >5,100 MILLION lb COPPER +5 IRON ORE BILLION TONNES www.optiro.com contact@optiro.com +61 8 9215 0000


www.skillings.net | 3
07 Mining Automation The Path To Sustainability MINING EQUIPMENT 34 World’s First Hydrogen-Pow ered Haul Truck Could Contribute To A Cleaner Mining Industry MINING FINANCE 10 Mining Projects in Latin America Face the Brunt of Inflation 18 US Steel Iron Ore Could Bring New Boom MINING JOBS 06 Hiring Levels In The Mining Sector Expected To Increase 22 Mines To Create 4,000 New Jobs in Zimbabwe 14 Deploying Artificial Intelligence To Help Fill The Short-Term Essential Minerals Gap 20 Career Prospects for Mining Engineers 21 Biden-Harris Administration Announces More Than $109M Support To Create Jobs 22 ArcelorMittal Creates Jobs in Liberia MINING TECHNOLOGY 38 Smart Technology Drives Promising Market Growth for Global Mining Automation SPECIAL FOCUS 36 Angola Set To Become Globally Competitive Mineral Producer 28 Implementing ESG During A Recession STATISTICS 46 October 2022 crude steel production 47 Crude steel production SURFACE MINING 06 Indian Government Accred its Thirteen Private Companies To Explore For Minerals UNDERGROUND MINING 05 Queensland Acland Coal Mine in Aus tralia Given $1Billion Adrenaline Shot 24 Biden Says Coal Plants ‘Across America’ Will Be Shut Down: Faces Backlash 27 US Mines More Coal In The West, But The East Employs More Workers 40 -2022 ANNUAL INDEX
THE LEAD
CUSTOMER SERVICE/ SUBSCRIPTION QUESTIONS:
For renewals, address changes, e-mail preferences and subscription account status contact Circulation and Subscriptions: subscriptions@Skillings.net Editorial matter may be reproduced only by stating the name of this publication, date of the issue in which material appears, and the byline, if the article carries one. www.skillings.net
SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW (ISSN 0037-6329) is published monthly, 12 issues per year by CFX Network, 350 W. Venice Ave. #1184 Venice, Florida 34284 Phone: (888) 444 7854 x 4. Printed in the USA. Payments & Billing: 350 W. Venice Ave. #1184, Venice, FL 34284.

Periodicals Postage Paid at: Venice, Florida and additional mail offices. Postmaster: Send address changes to: Skillings mining review, 350 W. Venice Ave. #1184 Venice, Florida 34284. Phone: (888) 444 7854 x 4. Fax: (888) 261-6014. Email: Advertising@Skillings.net.

UNITED STATES $72 Monthly in US Funds $109 Monthly in US Funds 1st Class Mail OUTSIDE OF UNITED STATES $250 US Monthly for 7 - 21 day delivery $335 US Monthly for Air Mail Service SUBSCRIPTIONS SKILLINGS
NEWS ROOM
Monthly Magazine SMR Americas Monday Global Skillings Wednesday Skillings Equipment Gear Friday All funds are monthly $4.95 USD per month publisher CHARLES PITTS chas.pitts@skillings.net managing editor SAKSHI SINGLA sakshi.singla@skillings.net editor-in-chief JOHN EDWARD john.edward@skillings.net creative director MO SHINE mo.shine@skillings.net contributing editors ROB RAMOS AALIYAH ZOLETA MARIE GABRIELLE media production STANISLAV PAVLISHIN media.team@cfxnetwork.com media administrator SALINI KRISHNAN salini.krishnan@cfxnetwork.com director of sales & marketing CHRISTINE MARIE advertising@skillings.net profiles in mining mining.profiles@skillings.net general contact information info@cfxnetwork.com 2022 DECEMBER VOL.111. NO.12 Skillings Mining Review of CFX Network LLC, publishes comprehensive information on global mining, iron ore markets and critical industry issues via Skillings Mining Review Monthly Magazine and weekly. SMR Americas, Global Skillings and Skilling Equipment Gear newsletters.
MINING REVIEW
Digital
4 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022
Queensland Acland Coal Mine in Australia
Given $1Billion Adrenaline Shot
BY ROBEL RAMOS
The region, where the unemployment rate is approximately 5.5%, will receive a $1 billion aid and will include 600 jobs on offer.
Initial earthworks have already started in the Acland Coal Mine, but New Hope hasn’t launched recruitment for the time being. Dave O’Dwyer, General Manager of New Hope, said that there was already significant



interest in jobs. O’Dwyer said that some pre vious employees and engineers had hinted at going back to the region to work in the mine.
"A lot of people had moved and worked in the Bowen Basin…doing long commutes…
away from their families," he said. "Some of our engineers went right up to Moranbah on a 10-day roster."
Around 80 to 100 workers are expected to start working in the mine early next year. More than 400 employees will be required when the mine becomes 100% operational. A large number of former New Acland Coal Mine Workers had shown interest - poten tially including Junior mining engineers who had previously been fired between 2019 and late 2021 when the reserves of coal were exhausted.

www.skillings.net | 5
Twelve years afTer The iniTial proposal, The conTroversial Acland Coal Mine extension has been given the green light to proceed. This development means additional jobs for the local economy.
Indian Government Accredits Thirteen Private Companies To Explore For Minerals
JOHN EDWARD
The Central Indian Government announced on November 8, 2022 that it had accredited thirteen private agencies to conduct mineral exploration in the country.
The goal of the Mines Ministry's privatization plan is to boost the economic potential of the mining industry and to open up new job opportunities. The Ministry aims to achieve the same by including more agencies in mineral prospecting.
“With the amendment of Mines & Minerals (Development & Regulation) MMDR Act in 2021, private agencies can also participate in exploration for the mineral sector after getting duly accredited by QCI-NABET (National Accreditation Board for Education and Train ing of the Quality Council of India). So far, 13 private agencies have been accredited and subsequently notified by the Central Govern ment," the Ministry declared in a statement.
Currently, there are twenty two government organizations actively engaged in mineral prospecting. Any private exploration agen cies who are interested will be “…required to obtain accreditation in accordance with the scheme and thereafter apply to the ministry for their notification under the second pro viso to sub-Section (1) of Section 4 of the Act," the Mines Ministry stated. The development is expected to speed up exploration and to increase the number of explored blocks available for auction.
Hiring Levels In The Mining Sector Expected To Increase
 MARIE GABRIELLE LAGUNA
MARIE GABRIELLE LAGUNA
when compared To The same monTh lasT year, The proporTion of mining sector operations and technologies businesses hiring for future work-related positions increased, with 43.5% of the companies in the analysis recruiting for at least one such position.
T his latest figure was higher than the 40% of companies that were hiring for future work-related jobs a year ago, but it was lower than the 52.5% figure in the previous months of 2022.
In terms of the percentage of all job openings that were linked to the future of work, related job postings fell - with 2.4% of newly posted job advertisements being linked to the topic. This latest figure was higher than the 1.9% of newly advertised jobs that were linked to future employment in the same month a
year ago. Many researchers have detected the future of work as a key disruptive force that companies will face in the coming years.
Companies that excel in these areas and invest in them now are better equipped for the future business landscape and better equipped to deal with unforeseen challenges.
It is perhaps promising to note that mining industry operations and technology firms are currently hiring for future work positions.
6 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022
Mining Automation The Path To Sustainability
AALIYAH ZOLETA
It goes without saying that mining involves a significant amount of risk. Continuous improvements in terms of tech nology and machinery are needed to ensure that the competi tive demand of metals is met in a safe manner.
According to GlobalData’s Thematic Research, robotic technology is indispensable for any mining company which aligns itself with the goals of safety,
productivity and sustainability. Mining automation has increased the efficiency and productivity of different mines around the world. It has also helped to ensure the

safety of workers in the workplace while still maintaining low mine operating costs.
There are many instances where technol ogy has saved a large number of lives. For instance, in 2018, an over-pressurized water pipe was detected at the BHP Nickel West drill mine.
Together with the robotics expertise of Woodside and Deakin University, the com pany was able to cut the pipe without having
www.skillings.net | 7
someone go through the tunnel. The entire operation involved working with a robot from a safe distance as it was a risky affair. Because of the robot, the company was able to resolve the issue within two weeks.
Gudai-Darri: Three steps ahead
Rio Tinto launched their most technologicallyadvanced mine in 2022 in the Pilbara region of Australia. The company was able to optimize mine safety and productivity in terms of ore sampling and the distribution of parts needed for the mine.


Rio Tinto’s mine is expected to last 40 years with an annual production of 43 million tons. Together with Caterpillar, Rio Tinto will develop new autonomous water carts that will be used for dust suppression, assess road dryness, and dispense water automatically.
“We’ve worked closely with both the Banjima and Yindjibarndi People through the planning and development stages of Gudai-Darri and we look forward to partnering with them into the future to ensure the project achieves
significant social and economic benefits. Gudai-Darri represents a step-change in the deployment of automation and technology within our iron ore business and a fantastic demonstration of the talent, ingenuity and capability that exists in Western Australia, a region which is now known globally for its technical excellence and innovation,” said Rio Tinto Iron Ore Chief Executive Simon Trott.
Trott added, “Gudai-Darri's combination of data and analytics, machine learning and automation, will make this mine safer and more productive. Gudai-Darri is our first greenfield mine in the Pilbara in more than a decade and a multi-billion-dollar invest ment in the State of Western Australia that will operate for decades to come.”
There are a lot of different advancements and innovations in Gudai-Darri such as
8 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022 THE LEAD
Modern technology, expert analysis and digital solutions will help lower water and energy use and reduce waste–and FLSmidth and ABB can really move the needle in this area,” said Mikko Keto, Group CEO, FLSmidth.
trucks that have sensors that provide live dig face progression and accurate assess ments of existing ground conditions that help improve safety of the workers. They also have autonomous trains which will be used for transporting heavy equipment and different types of ore.
The company also has the first notable buc ketwheel reclaimer, a solar farm which consists of 83,000 solar panels, and paper less field mobility. The solar panels’ capacity is 34MW - enough to supply a third of the mine’s average electricity demand.
HeartCore signs with Transcosmos Digital Technology
HeartCore Enterprises recently announced their partnership with Transcosmos Digital Technology Inc. for the process mining tool
Apromore. HeartCore will mostly cater to Japanese enterprises and help with their digital transformation.
“We are pleased to sign a licensing agreement with TCDT, a company that understands the magnitude and importance of digital trans formation.Though the prevalence of process mining is in its nascent stage, the growing concern among business managers strug gling to optimize complex operations led us to pursue our initial exclusive reseller agree ment with Apromore in June of last year.
We intend to continue partnering with companies such as TCDT, as we expand our go-to-market efforts. We remain laser focused on leveraging our exclusive right to resell Apromore in Japan, as part of our own process mining service and plan to continue taking advantage of synergistic opportunities to scale our Digital Transformation initiative,” CEO Sumitaka Kanno (Yamamoto) stated.
ABB, FLSmidth to help mining companies de-risk operations
ABB and FLSmidth have joined forces to lower operating costs and ensure safety of laborers in the workplace. The agreement was finalized at the FT Mining Summit in London.

According to Joachim Braun, division president, ABB Process Industries, this col laboration is very important to the mining industry and will help achieve the targets outlined in the UN Paris Agreement. He also added that these two companies have chosen to work together during these times to help customers achieve their business goals and carbon-free operations that will benefit their workers.
“FLSmidth and ABB already have many of the building blocks for carbon-free, resource-op timized operations. By assessing how to combine and integrate these technologies and our respective expertise we will, together
with our customers, accelerate transition in mining operations. Mining is essential in the energy transition. Meanwhile, the mining industry is facing unprecedented challenges due to declining ore grade and high demand as it develops new sites, while also being asked to make existing operations more sustainable.
Modern technology, expert analysis and digital solutions will help lower water and energy use and reduce waste–and FLSmidth and ABB can really move the needle in this area,” said Mikko Keto, Group CEO, FLSmidth.
FLSmidth is known for providing sustain able productivity to the mining industry with market-leading technology and prod ucts that help their customers reduce their environmental footprint. The company introduced ‘MissionZero’ in a bid to make mining sustainable by 2023 in terms of technology, equipment, mineral processing expertise, automation, electrification and digital solutions.

www.skillings.net | 9
Mikko Keto, Group CEO, FLSmidth (left) shaking hands with Joachim Braun, Division President, Process Industries, ABB
Mining Projects in Latin America Face the Brunt of Inflation
 JOHN EDWARD
JOHN EDWARD
in a worrying developmenT, mining projecTs across laTin america are stalling in the face of rising inflation and inflating production costs. An article published by Bnamericas stated that escalating inflation has hit mining projects across Latin America and driven costs higher. The extent of the problem can be gleaned from the fact that mining companies are being forced to ‘dig in’ to ensure continued impacts in 2023.
The Russian invasion of Ukraine has only worsened the problem by driving up the prices of natural gas, diesel, and energy. Mining companies have also highlighted that the steep increase in the cost of materials like equipment, tires, reagents, and steel have added to their woes.
Additionally, companies are also facing the brunt of rising labor costs in the aftermath of the Covid-19 pandemic. Inflationary pres sures have also led to spikes in shipping and freight costs.
10 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022 MINING FINANCE
Truck at Chuquicamata, world's biggest open pit copper mine, Calama, Chile.
“Cost inflation is definitely occurring across the [mining] industry,” opined Joe Bormann, Fitch Ratings’ head of Latin America corpo rate ratings. “At a general level, it’s happening to every company out there.”
What is more troubling perhaps is the fear that the situation might not get better any time soon. “As we look ahead, we expect that inflationary pressures and the impacts from a competitive labor market will persist into 2023, resulting in production levels and unit costs that will be similar to this year,” Newmont CEO Tom Palmer stated.
Needless to add, mining projects across Latin America are feeling the heat of the situation. In September 2022, Newmont pushed back a construction decision for the US$2.0bn Yanacocha Sulfides gold-copper project in Peru by two years to 2024.

The decision was taken after a review of the project scope. “As part of its review, Newmont considered the unprecedented and evolving market conditions, including the continued war in Ukraine, record infla tion rates, the rising prices for commodities and raw materials, prolonged supply chain disruptions and competitive labor markets,” the company said in a release.
The trend of rising capex estimates can be seen in other projects as well. On the basis of the current cost environment and estimate accuracy, Teck Resources and new JV part ner Agnico Eagle Mines said in September that development capex for the San Nicolás copper-zinc project in Mexico could go up to anywhere near the US$1-1.1bn range. This figure is significantly higher than the previ ously forecast US$842mn.
Elsewhere in Mexico, Torex Gold is expecting higher construction costs for its Media Luna gold-copper project. The project was esti mated at US$848mn in a March feasibility study in comparison to the US$496mn in a 2018 PEA.
According to Torex, the March estimate is, in part, a reflection of the current inflationary environment. “We want the project to be palatable to the market but we also want it to be credible, realistic, and something we can deliver on,” admitted CEO Jody Kuzenko in July.
Despite this worrying inflationary envi ronment, some companies have managed to keep their project costs in check. For instance, SilverCrest Metals is in the process of ramping up operations at its US$138mn Las Chispas silver-gold mine in Mexico.
The mine started production ahead of sched ule and was under budget in July. Similarly, Minera Alamos highlighted low-capex devel
opment in its Cerro de Oro PEA earlier in October. The project’s pre-production capital costs were pegged at US$28.1mn for an asset which is expected to produce 58,400oz/y gold over an 8.2-year mine life. The company president Doug Ramshaw had attributed the low capital intensity of the project, in spite of rampant inflationary pressures, to the com pany’s sound business model in a release.
All isn’t well however. Inflation has been tagged as the key driver in Pan American Silver’s decision to suspend underground operations at its Dolores gold-silver asset in Mexico. The company said in August that the decision came in the backdrop of a shortfall in grades which triggered an analysis for impairment.
Needless to add, mining projects across Latin America are feeling the heat of the situation.
www.skillings.net | 11
In September 2022, Newmont pushed back a construction decision for the US$2.0bn Yanacocha Sulfides gold-copper project in Peru by two years to 2024.
Rising costs have also pushed First Majes tic Silver to reduce its spending plans. The company focuses on silver production in Mexico and is pursuing the development of its existing mineral property assets.
First Majestic Silver presently owns and operates the San Dimas Silver/Gold Mine, the Santa Elena Silver/Gold Mine, and the La Encantada Silver Mine.
Rising production costs have further exac erbated the problem. According to Chilean copper commission Cochilco, the higher production costs across the country’s copper assets are linked to global inflation and a reduction in output.
Chile happens to be the world’s top copper mining country. In a worrying development, cash costs of larger producers increased by US$0.183/lb in H1, compared to the same period last year, with 16 smaller operations seeing a much steeper rise, up US$0.542/lb.
These higher costs will eventually be passed on to consumers despite the fact that mining companies are likely to benefit from the strong prices of industrial and precious metals in comparison to historical averages.
Metals prices are increasing partly due to global shortages associated with slow proj ect development, mine disruptions, and growing demand.
It is important here to note that consumption of metals like copper and lithium is expected to increase significantly in the coming years with the increasing push towards renewable energy and electric vehicles.
“With the shortage of metals out there, most of those increases in price are going to be transferred on to the end users,” Bormann added. “Buyers out there are just going to pay for it and at the end of the day they are just going to push [rising costs] onto consumers.”
What Effects Will The Global Energy Crisis Have On Crypto Mining Markets?
here is no denying that the world is currently experiencing an unprecedented energy crisis. This crisis has been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic and the Russian invasion of Ukraine. This has resulted in severe shortages and sharp increases in the price of oil, gas, and electricity in nations around the world – especially in Europe and North America.
Limited gas supplies have drastically increased the cost of necessities like fertilizer. In addition, they have also led to a greater reliance on coal and other natural resources. Europe alone had a 14% increase in coal usage last year and another 17% increase is anticipated by the end of 2022. European gas prices are currently approximately ten times higher than their average level over the previous ten years, hitting a record high of over $335 per megawatt-hour in late August. On a related note, the recently released winter fuel estimate for 2022 from the United States Energy Information Administration predicts a staggering 28% increase in average fuel prices for Americans over the current year, reaching a staggering $931.
With such alarming data available in the public domain, it is important to investigate how this prolonged energy deficit may impact the crypto industry and whether its negative impacts will abate any time soon.
Experts Weigh In On The Subject
The global economy is in bad shape according to Matthijs de Vries, founder and chief technical officer of AllianceBlock – a blockchain company that bridges the gap between decentralized finance and traditional finance. He recently told Cointelegraph that a number of factors – such as the power crisis, an impending recession, surging inflation, and rising geopolitical tensions – are to blame.
He added that, “These problems are connected, particularly in the way that capital enters and exits businesses that have an impact. The capital that flows into and out of the digital asset industry is negatively correlated with the macroeconomic environment. The blockchain’s incentivization processes can only function as long as there is this liquidity. Therefore, if there is a lack of liquidity, miners will have fewer transactions to confirm, lower fees, and fewer incentives.”
De Vries also thinks that rising energy prices may give miners greater motivation to switch to Ethereum 2.0’s validator ecosystem, which uses a proof-of-stake mechanism that is much more energy-efficient.
Even though the current energy crisis will have a considerable impact on miners, there is still some hope that the present macroeconomic circumstances will favor the crypto business.
T
12 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022 MINING FINANCE
HALCOR PRODUCTS
Copper tubes with or without lining or industrial insulation for applications in:
• Drinking water and heating networks
• Underfloor heating and cooling
• Gas and medical distribution networks gases
• Cooling and air conditioning systems
• Solar energy applications
• Various industrial applications
The copper segment of ElvalHalcor S.A. is composed of six subsidiaries and seven associates/joint ventures, based in Greece, Belgium, Bulgaria, Romania and Turkey, while it operates a total of five production plants in Greece, Bulgaria and Turkey.
The copper segment of ElvalHalcor S.A. develops and distributes a wide range of products, including copper and copper-al loy rolled and extruded products with Halcor being the sole producer of copper tubes in Greece. High quality in production

Halcor is the copper tubes division of ElvalHalcor S.A. and together with four more companies form the copper segment of ElvalHalcor S.A. that specializes in the production, processing and marketing of copper and copper alloys products with dynamic commercial presence in the European and global markets. For more than 80 years, Halcor has been offering innovative and added-value solutions that meet contemporary client demands in fields, such as plumbing, HVAC&R, renewable energy, architecture, engineering and industrial production.
is achieved through strict controls applied throughout the production process. With a consistent quality focus, the company implements an ISO 9001:2015 Certified Quality Management System and leverages high technologies and expert staff.
As a result of the Group’s strategic invest ments in research & development, Halcor is recognized as one of the leading copper producers globally, setting new standards in copper processing. The company main tains a consistent focus on quality and

environmental protection and a strong commitment to the principles of sus tainable development. In this context, all production facilities in the Group’s plants leverage advanced technologies to bring in the market innovative products that are energy efficient and environmen tally friendly.
For more information, please visit our web site www.halcor.com
www.skillings.net | 13
Deploying Artificial Intelligence To Help Fill The Short-Term Essential Minerals Gap
MARIE GABRIELLE LAGUNA
sofTware based sysTems ThaT use daTa inpuTs To decide for themselves or to assist people in making decisions are referred to as artificial intelligence (AI) systems. The use of AI will be crucial to the survival of businesses of all sizes and in all industries within a few years.

A part from growing environmental challenges, there are significant energy security issues in many parts of the world. This is taking place in the backdrop of rising energy costs, partly as a result of supply chain issues influenced by the ongoing crisis
in Ukraine. In Europe, where natural gas is heavily used for heating and cooking as well as the production of electricity, this effect is amplified. Thus, the market becomes more susceptible to supply shortages. Governments around the world are being
compelled to improve their domestic resilience and energy security through the provision of clean energy in order to protect consumers from significant financial effects.
Additionally, this is hastening a change in energy production to help limit global warm ing below 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Nevertheless, the demand for mineralsparticularly vital minerals like lithium, cobalt, copper, nickel, and graphite - is anticipated to rise significantly because of the energy tran
14 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022 SPECIAL FOCUS
sition. Predictions state that by 2040, there will be a four-fold increase in the number of key minerals needed for renewable energy technology.
For the mining sector, this is a breakthrough. However, the industry must develop new strategies to boost productivity and efficiency in order to meet rising demand and to close the supply gap.
In order to maintain its current permits and obtain new ones, the mining sector will also need to keep its environmental and climate footprints under stringent control.
The Landscape for Mining Businesses Using Artificial Intelligence
In the mining sector, AI is more crucial than ever due to declining yields and adverse environments. Every stage of the mining value chain - from exploration to extraction, processing, and even marketing - can be significantly impacted by AI.
With the potential to maximize ore pro cessing, AI is making systems smarter and capable of extracting more value from already-existing resources. AI can even benefit the environment by improving the remote targeting of rich mining resources. This results in the reduced need for pointless excavation which can be extremely harmful to the environment.

The Effects Data May Have
Every mineral processing facility has inefficiencies because of the intrinsic geological variability of the ore that these facilities deal with - irrespective of whether such a facility processes 50,000 ounces of gold annually or 400,000 tons of copper annually.
Even with mineral processing facilities working towards increasing productivity, the mining sector faces a number of diffi
culties including growing costs, fluctuating commodity prices, and variability in operating procedures.
Concerning the effect of mining on natural resources, there is another troubling factor. Roughly 3 billion tons of ore are extracted annually and the mining sector accounts for 10% of the energy utilized globally. Fur thermore, mining operations utilize over 4 billion cubic meters of water annually. The increasing demand for minerals and metals will only exacerbate the effect on our natural resources unless we take a dramatically different and climate-smart approach.
Miners use numerous systems and data bases to manage their processes in an effort to boost efficiency. However, the collected data remains vastly underutilized in a sig nificant number of cases. According to the findings of recent McKinsey studies, mining corporations only utilize less than 1% of the data collected by their equipment and tools. As a result, many petabytes of data are not utilized for operational decision-making and instead languish in silos.
www.skillings.net | 15
In the coming years, digitization may help close the gap between the supply and demand of essential minerals. A 3% to 5% boost in metal recovery utilizing AI applications would increase our potential to provide an extra 450,000 tons of copper annually, valued at $3.2 billion, according to the earlier estimates for copper mine production.
Excellence in Next-Generation Operations

Mining executives are increasingly using artificial intelligence (AI)-based technology to plan for future operations.
Digital twins, autonomous systems, and deep learning neural networks are a few of the technologies that reveal hidden correla tions between various process parameters to reveal hidden insights into process performance.
This is especially useful for the mining industry due to the dynamic nature of its processes, the challenging working environ ment that causes data loss and data quality problems, and the inherent geological uncer tainty linked to different ores.
When data is fully utilized, the deployment of an integrated physics-informed machine learning model (scientific AI) through a realtime software environment can uncover concealed insights, provide superior forecasts, and encourage efficiency improve ments through real-time optimization.
Scientific AI-driven software technologies can improve organizations' decision-making processes to deliver more significant busi ness outcomes when properly integrated into workflows that traditionally require human intelligence. It is important to note, however,
that there is no one-size-fits-all technological solution to solve every industry challenge. The improvements in communication are a fantastic illustration of how digitization may increase productivity. About 53% of the
energy consumed in mines is used in "the process of crushing and grinding ore." Using AI technologies for real-time monitoring and mill prediction has already demonstrated the potential to boost throughput while lowering
energy consumption. This is achieved by safely pushing equipment to its maximum operational capacity.
Effect of Efficiency on the Supply of Essential Minerals
Efficiency gains have a big impact on the mining industry. As an example, copper is one of the most widely used metals in the world with demand coming from a variety of sectors including renewable energy and building.
In the mining sector, AI is more crucial than ever due to declining yields and adverse environments. Every stage of the mining value chain - from exploration to extraction, processing, and even marketing - can be significantly impacted by AI.
16 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022
SPECIAL FOCUS
The top 20 copper mines in the world today have an annual production capacity of about 9 million tons.
In 2020, this accounted for 44% of global copper production. However, given that the demand is expected to rise by 31% between 2020 and 2030, this present source of supply simply won't be enough.
In the coming years, digitization may help close the gap between the supply and demand of essential minerals. A 3% to 5% boost in metal recovery utilizing AI applica

tions would increase our potential to provide an extra 450,000 tons of copper annually, valued at $3.2 billion, according to the earlier estimates for copper mine production.
This is the equivalent of the yearly output capacity of Peru's Las Bambas Mine - one of the world's top eight copper producers.
Improvements like these give an already strangled industry some breathing room, especially in light of the fact that "the average mine takes 15 years to bring into production." Millions of tons of minerals, including essen
tial minerals, are already needed to support a sizable transition to renewable energy for a low-carbon future.
The mining sector can boost productivity, cut waste, and avoid using energy from non-renewable resources by implementing next-generation AI-based software technol ogies such as scientific AI.
fryberger.com Equipping the mining industry with legal services since 1893. ›› Paul Kilgore ›› Paul Loraas ° MINING & MINERALS LAW ° ∙ Mineral purchase agreements, leases and options ∙ Land assembly and mineral rights acquisition ∙ Severed mineral registration and title work ∙ Environmental permitting and compliance
www.skillings.net | 17
US Steel Iron Ore Could Bring New Boom
us sTeel is seT To produce TaconiTe pelleTs ThaT could poTen tially save the iron ore mining industry and create more job opportunities. For almost a century, Minnesota mines have produced iron ore not just for US Steel mills but also for other major corporations. These mills then turn ore, coal, and limestone into cast iron and eventually steel.
Kangas, Director of the Natural Resources Research Institute at Coleraine, part of the University of Minnesota. Duluth. “This is a huge step forward for Minnesota’s iron ore industry,” he added.
Cleveland-Cliffs, the most significant player on the Iron Range, is already producing highgrade iron ore pellets.
The future of the Iron range depends on whether these two major players, which have been associated with blast furnace steelmak ing, make it or not in this new industry. It is important to note that the mines found in this region have always been in the hands of their steelmakers.
“We are on Pins and Needles on the Rail Belt as the Steel Industry Turns Around [electric furnaces]. Are we going to be part of the long-term future of the steel indus try? That worries me,” said John Arbogast. Arbogast is the 11th district representative for the United Steelworkers of America, which represents workers at all but one of the state’s six taconite operations.
Minnesota’s taconite industry is still a pillar of the Iron Range economy despite having diminished from its prime.
In its heyday, this industry contributed about five thousand jobs. This figure may have dwindled to four thousand jobs but, on a positive note, has remained steady for the last two decades. The mining industry provides one of the highest-paying jobs in the country and the industry forms the Iron Range’s tax base.
ROBEL RAMOS
However, this process is becoming obsolete as cheaper and more energyefficient plants utilizing electricity and scrap metal become the new norm. Furthermore, as governments increasingly call for greener and cleaner alternatives, traditional steelmaking’s future is beginning to look a bit uncertain. The Pittsburgh-based company is
set to put in $150 million in its Keewatin plant. This plant produces high-grade iron ore to power electric furnaces or mini-mills. These mini mills create high-quality steel and need high-quality iron to supplement scrap metal.
“The biggest advance in modern iron ore processing technology is what’s happening right now in the Iron Range,” said Kevin
Keewatin mayor Mike LaBean said, “Mining is still the straw that stirs the drink.” LaBean was a miner until he lost his job in the early 1980s. Keetac, a site near Keewatin City Hall, is one of the many taconite sites in the area. It was built between the mid-50s and mid-70s and is the smaller of the two Iron Range mining and processing opera

18 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022 SURFACE MINING
tions owned by US Steel. Keetac has 400 workers and will continue producing tra ditional seeds. Taconite is about 30% iron and is mined from the Keetac site and then fed into a large crusher. The iron is culled from the pulverized ore using magnets. It is then molded with clay into smaller pellets containing approximately 66% iron.
In August, US Steel started expanding to take this process one step further. If Kee tac’s new wing begins operating by 2024, the facility will still produce new pellets with 68% to 69% iron. They will also have less silica as compared to traditional pellets
thereby making them more suitable for use in electric furnaces.
Mike Bakk, director of operational readiness at the iron ore factory in Minnesota said, “This is probably the most exciting thing that has happened in the Iron Range in 50 years.”


Electric furnaces are increasingly gaining a foothold in the industry. In the 1980s, electric furnaces gained traction - especially in the US where scrap metal is abundant. First, they produce low-grade steel products like rebar for reinforced concrete. However, the influx of newer technology prompted small-scale

mills to enter the premium steel market. By 2021, 71% of US steel production comes from electric furnaces - a 47% increase from 20 years ago. These figures come from Carnegie Mellon University’s Iron and Steel Research Center in Pittsburgh.
Traditional steelmaking’s share in the market has plummeted and the number of blast furnaces in the country has dipped from 60 in 1990 to 21 in 2021. Small-scale mills employ electrodes in order to melt scrap metal, together with pig iron and DRI or direct reduced iron, both of which are critical in making high-quality steel.
www.skillings.net | 19 Proud to be your reliable partner. We have long supported the region’s mining industry by providing safe, reliable and competitively priced electricity. In 2021, half of the energy we provide to all of our customers will come from renewable sources. Together, we power northeastern Minnesota’s economy. mnpower.com/EnergyForward 19260
A new “direct reduced” iron pellet from US Steel and Cleveland-Cliffs is being designed for use in DRI furnaces, creating a product with about 95% iron.
In the US, there are three DRI plants. One is owned by Cleveland-Cliffs and is located in Toledo, Ohio. This plant uses DRI for its electric and blast furnaces.
US Steel is contemplating disposing the reduced pellets directly to DRI manufac turers. They also plan to build their own DRI plant.
Kevin Lewis, US Steel’s vice president of investor relations, said, “It is not a matter of if, it is a matter of when and where it comes with DRI.” He also said US Steel “did not go into much site consideration for the DRI plant.”
The Iron Range would like to have a DRI plant and Cleveland-Cliffs has put in $1 billion in its DRI operations.
To produce grain for its DRI plant, Cleve land-Cliffs in 2019 shelled out $100 million in the North Shore taconite operations in Silver Bay. However, the plant and the Babbitt mine that supplies it has been decommissioned.
Steve Mekkes, senior engineer for the Min nesota Department of Natural Resources said, “You can’t judge the market for DR pellets based on what Cleveland-Cliffs is doing because they’re making their own internal business decisions.”
Electric furnaces will continue to benefit considering they are less harmful to the environment as compared to carbon diox ide-emitting blast furnaces.
“Most blast furnaces shut down because the CO2 concentration is so high,” said Chris Pistorius, a fellow at Carnegie Mellon’s Iron and Steel Research Center.
Career Prospects for Mining Engineers
BY ROBEL RAMOS
a loT of people sTill Think of TradiTional miners when They talk about mines and the mining industry. The truth, however, is that mining is more than just pickaxes, hard-hats, and getting down to a mineshaft on a lift to mine and haul gold, coal, and other precious metals.
The influx of modern technology has drastically changed how things work - especially in dangerous workplaces typically associated with the mining industry. These changes , however, have prompted industries to rethink their traditional practices. It goes without saying that organizations are adopting better and more modern strategies in order to ensure survival, growth, and productivity.
The rise of technology has also swayed companies to hire tech-savvy senior roles like planning engineers, machine learning engineers, geologists, and senior mining engineers to name a few. Technological advances have proven to be efficient thereby helping com panies reduce costs while increasing productivity.
In 2019, Market Intelligence discovered that companies with female CEOs saw an increase of 20% in stock price momentum. Diversity and inclusion in the industry are the future. For individuals trying to venture in this industry, the career path for mining engineers within the domain may differ but the future is bright.
Mining Engineer
Geology
Mining and Mineral Surveying
This professional is responsible for assessing the safety, feasibility and productivity of potential locations. They develop the design of the mine and also mining equipment. To be a mining engineer, one has to have a degree in one of the following: Civil Engineering Minerals Surveying Mine and Quarry Engineering
In case an individual possesses any of these degrees, a multitude of career paths open up including:
Junior Mining Engineer Mine Planning Engineer Senior Mining Engineer Mine Supervisor Resident Manager
MINING JOBS
20 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022
Biden-Harris Administration Announces More Than $109M Support To Create Jobs
BY JOHN EDWARD
The Biden-Harris Administration announced a $109.48 million plan as part of President Biden’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Law intended to create “goodpaying union jobs” and to “catalyze economic opportunity” on November 15, 2022. The aforementioned goals will be achieved by reclaiming abandoned mine lands (AML)
in Alabama, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas and New Mexico. The Department of the Interior has made $725 million available to 22 states and the Navajo Nation in fiscal year 2022. More than $533 million were announced in awards in October for Kentucky, Maryland, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Virginia and West Virginia. Funding will be awarded to additional eligible entities on a rolling basis as they apply.

“Through President Biden’s Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, we are making a once-in-a-generation investment to clean up environmental hazards that are harming local communities,” said Secretary Deb Haaland.
“Reclaiming and restoring these sites will create jobs, revitalize economic activity, and advance outdoor recreation. I am so excited about what we can do with these new resources, today and for future generations.”
It is important to note that millions of Americans live within just one mile of an abandoned coal mine or orphaned oil and gas well across the country.

SOLVING YOUR MOST COMPLEX CHALLENGES. With SEH, you are a true partner and collaborator. Engineers | Architects | Planners | Scientists 800.325.2055 | sehinc.com/subscribe
www.skillings.net | 21
Mines To Create 4,000 New Jobs in Zimbabwe
BY JOHN EDWARD
In an article for The Sunday Mail, Oliver Kazunga opined that mining companies were expected to create four thousand jobs in Zimbabwe thanks to US$1 billion capital expenditure programs in the sector.
According to the Chamber of Mines of Zim babwe, this projected growth represents an increase of 9 percent in new formal employment from the current figure of approximately 45,000 workers in the sector.

The mining industry is one of Zimbabwe’s key productive sectors and is responsible for bringing in 73% of foreign direct investment into the country. It also accounts for 83% of exports, 19% of government revenues, 2% of formal employment, and 11% of individual incomes. Keeping in mind the industry’s significance to the economy, the Second Republic - under
President Mnangagwa in 2019 - had launched a US$12 billion mining economy target to be achieved by 2023.The envisaged milestone will depend upon increasing production through expansion projects, reopening of closed mines, and the launch of new projects. By the end of 2022, the mining sector is expected to grow to a US$8 billion economy as compared to US$5.3 billion last year.
Growth of Oilsands Mine in Recruiting Female Equipment Operators
MARIE LAGUNA
'The more equal we feel ouT here, The nicer iT is for all of us,' says Robin Hebbard.Robin Hebbard was one of the handful of women who worked as heavy equipment operators and simulator trainers at Syncrude's Aurora mine in 2007.
Female workers now account for roughly 30% of the workforce at the Aurora site. The increase was most noticeable in the locker room, which had 135 lockers and 180 women. "We saw two to three women per locker," Hebbard explained. She raised the issue with her director, and the corporation switched one of the men's locker rooms with the smaller women's locker room in December, freeing up 213 lockers. "It's really great to have a remedy to the issue and a space for all the women to feel comfortable," she said. "The more equal we feel out here, the better it is for all of us."
Hebbard credits the success of the Aurora site to programmes such as Women Building Futures, which provides support services to assist unemployed and underemployed women in discovering different careers. Women Building Futures collaborated with the Aurora site to recruit and support female heavy equipment operators, according to Thomson. Careers The Next Generation is also working to increase the number of women working in trades.
ArcelorMittal Creates Jobs in Liberia
With one of the best paying rates and consistent investment in programs that enrich its staff’s working experience, it comes as no surprise that ArcelorMittal’s workforce is growing steadily in Liberia.
In an article for GNN Liberia, Cholo Brooks opined that ArcelorMittal was a top-rated employer in Liberia. The company has nearly 3,000 employees and contractors in the country, out of which 95% are Liberians.
Partly owned by the Liberian Government, ArcelorMittal Liberia benefits the country on many fronts, including job creation, revenue generation, socio-economic development, and community development projects. Investing in the country and sharing the values of the communities where it operates are important priorities for the business.
MINING JOBS
22 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022



www.skillings.net | 23 FloLevel Technologies
Biden Says Coal Plants ‘Across America’ Will Be Shut Down
JOHN EDWARD
The White House scrambled to clarify President Biden’s declaration that an energy transition would mean shutting down coal plants. In an article for Bloomberg News, Anna Edgerton and Jennifer A. Dlouhy reported that the White House sought to reframe President Joe Biden’s comments on closing coal plants as part of a US “energy transition.”
On November 4, 2022; Biden had declared that coal plants were simply too expensive to operate. He had further added that he was inclined to shut “these plants down all across America" in order to transition towards more renewable sources of energy.
"I was in Massachusetts about a month ago on the site of the largest old coal plant in America," Biden mused at an event in Carls bad, California. "Guess what? It cost them too much money.

They can't count. No one is building new coal plants because they can’t rely on it. Even if
they have all the coal guaranteed for the rest of the existence of the plant.”
"So it's going to become a wind generation. And all they're doing is it’s going to save them a hell of a lot of money and using the same transmission line that they transmit ted the coal-fired electric on, we're going to be shutting these plants down all across America and having wind and solar power, also providing tax credits to help families buy energy efficient appliances, whether it's your refrigerator or your coffee maker, for solar panels on your home, weatherize your home, things that save an average, experts say, a minimum of $500 a year for the average
family," he added. Biden’s comments drew almost immediate criticism from different quarters including the mining industry and West Virginia Senator Joe Manchin.
The latter called the remarks “outrageous and divorced from reality.” The situation is particularly delicate because the US is days before midterm elections with Democratic congressional majorities at stake.
Republicans were also quick to criticize Biden for pursuing an energy policy that could cost American jobs. “We know how this ends,” Representative Steve Scalise, Republican of Louisiana, said on Twitter. “People lose their livelihoods. You pay more for energy.
A Department of Energy report published this summer had indeed shown massive job losses in the fuel industry. The annual U.S. Energy and Employment Report (USEER) stated that the coal industry lost 7,125 jobs in 2021 which reflected a reduction of 11.8% year-over-year.
24 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022 UNDERGROUND MINING
The backlash came just as the President was about to campaign in Pennsylvania which is a coal-rich state and has a long history as both a producer and user of the fossil fuel. Pennsylvania is also the battleground of a closely fought Senate race that could potentially determine control of the chamber. The neighboring states of West Virginia and Pennsylvania are the second-largest and third-largest coal-producing states in the US respectively.
White House Press Secretary Karine JeanPierre said in a statement that Biden’s comments “have been twisted to suggest
a meaning that was not intended” and that the President “regrets it if anyone hearing these remarks took offence.”
Jean-Pierre also went on to state that Biden recognized that coal had long powered the US economy. She also highlighted that Biden had worked with Manchin to bring jobs and federal funds to regions hit by the transition away from fossil fuels. “No one will be left behind,” assured Jean-Pierre.
However, the damage may have already been done. “Being cavalier about the loss of coal jobs for men and women in West Virginia
and across the country who literally put their lives on the line to help build and power this country is offensive and disgusting,” Senator Manchin said in a statement on November 5. He called for a public apology and declared that it was time that Biden learned “a lesson that his words matter and have consequences.”
The United Mine Workers of America also jumped to defend the coal industry’s role in the energy transition and in develop ing technology which would lower coal’s carbon footprint. UMWA President Cecil Roberts stated that Biden’s comments were

www.skillings.net | 25 Industrial General Contractor Specializing in Equipment Installation and Maintenance crmeyer.com 800.236.6650 Offices: Byron, GA Escanaba, MI Muskegon, MI Coleraine, MN Tulsa, OK Chester, PA Oshkosh, WI Green Bay, WI Rhinelander, WI Millwrighting Piping Ironwork Concrete Electrical Building Construction Design/Build Offices Nationwide l l l l l l l Boilermaking l
“disheartening”. He went on to invite the President to visit communities in West Vir ginia, Pennsylvania, and Kentucky that had been impacted by coal plants shutting down.
“It’s easy to talk about ending an industry that supports hundreds of thousands of jobs in Appalachia and the Midwest, but the reality of such an action is harsh,” Roberts declared in a statement.
For his part, Rich Nolan - Head of the National Mining Association - said that Biden’s com ments were “completely incompatible” with energy-driven inflation. Furthermore, he stated that the statements were not in tune with the needs of the electric grid in many parts of the US. Any action that contributes to the global energy crisis would be “reckless and unthinkable” he opined.
It is important to note that Manchin isn’t up for re-election this year. He also happens to be a rare Democrat who represents pri marily conservative constituents. Manchin had previously emerged as a key vote in the evenly split Senate when he helped to pass Democrat-only projects such as the Inflation Reduction Act. This was after he had initially blocked Biden’s Build Back Better tax-and-spending plan.
Manchin has come under fire recently from parts of the Democratic Party for holding up policy priorities and for refusing to end the filibuster which depends on a 60-vote majority to pass most bills. On November 5, his frustration with Biden boiled over as he publicly questioned the President’s credibility.
“Comments like these are the reason the American people are losing trust in Pres ident Biden,” Manchin said in a statement. “It seems his positions change depending on the audience and the politics of the day.”
Western Lenders Restrict Financial Services to Coal Miners
ROBEL RAMOS
when iT comes To mining, especially coal mines, now is boTh the best and the worst of times for coal miners. After years of steady decline, the demand for coal has finally made solid breakthroughs as Europe scrambles to find an alternative to Russian gas.
With the prices of coal hitting record highs, one would expect companies to expand their operations. However, projects are being either shelved or left behind as Western banks stand by climate pledges to restrict lending to the coal miners sector. The Chief Financial Officer at the Australian coal miner Coronado Global Resources Inc., Gerhard Ziems, said, “If you are a business with a bank right now, it is easier. If you want to build a new mine, forget it; that has become impossible.”
The lower-value thermal coal typically used in power plants traded above coking coal for the first time in June. Ziems added that this was a crazy scenario – akin to silver trading at a higher price than gold. Benchmark Australia Newcastle thermal coal was suffering at $50 per ton at the start of 2020 before spiking above $150 per ton at the start of 2022. Thermal coal further hit a record high at more than $400 per ton in September as countries tried hard to replace Russian gas.
However, with most Western banks under pressure from shareholders to stay true to their commitment to climate change, coal miners say they are having a hard time scouring for alternative financial backing to take advantage of the scenario.
For some mining companies, it has become difficult to even find a lender for simple financial assistance. Shortly after North American miner, Ben Creek Group was listed on London’s AIM in October 2021, Lloyds Banking Group withdrew its banking services to the company due to a change in policies related to fossil fuels.
The banking company said that it would stop financing miners that generate more than 5% of their revenue from thermal coal by the end of 2022. Managers of Ben Creek suffered from the rejection and had to wait for months before they were able to open an account at the State Bank of India’s branch in Britain, CEO Adam Wilson said to Reuters.
The chief executive of Ben Creeks said that no company had these problems five years ago. Lloyds did not provide any comments on individual client relationships. It is a similar scenario for Minergy Limited – a startup company listed in Botswana. The company is looking for a financial institution to fund its expansion projects.
26 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022 UNDERGROUND MINING
US Mines More Coal In The West, But The East Employs More Workers
The annual coal reporT by ajoT revealed ThaT abouT 60% of coal was produced in the western part of the United States in 2021. However, only 28% of workers in coal mines worked there. The differ ence is due to the technologies employed in the East and West - surface mines in the latter use massive mining equipment and machines to extract a large amount of coal using fewer workers.
BY ROBEL RAMOS
The report separated the US into two regions, East and West, divided by the Mississippi River. Before the 1970s, most of the coal in the country came from the East. However, starting in the 1970s, the production of coal started expanding in the West due to the following reasons:
New emissions laws and regulations
New large-scale surface mines at the Powder River Basin in Wyoming, and other areas in the West.
Lesser freight rail shipping costs. It is important to note that coal is basically used for electricity generation in the US. However, the Clean Air Act of 1970, and subsequent amendments in 1977 and 1990, restricted sulfur emissions from power plants powered by coal.
In order to meet the regulations, these power plants have to burn low-sulfur coal which is normally found in the West. This resulted in an increased demand for low-sulfur coal,
especially in the Powder River Basin. In 2021, coal mine workers in the West produced 16 tons of coal every hour, significantly higher than their counterparts in the East where workers produce only 4 tons per hour of coal.
The difference can be attributed to the size of the coal mines in the West which are often large, open-pit operations that tap thick coal seams close to the surface. This lets miners from the West utilize super-sized draglines, shovels, and monster trucks, allowing com panies to extract and haul more coal with relatively fewer workers.
In the East, mines are smaller, underground operations with thinner coal seams which are often deeper and more difficult to extract. And despite deploying advanced technology like the longwall mining systems, mines in the East are not only laborious and toilsome compared to their western counterparts, they also have a lower productivity rate.
The new business environment in the rail road industry following the country’s railroad deregulation prompted railroads to inno
vate and utilize dedicated unit trains that typically load a single commodity directly to its destination. These unit trains let coal from the western side be transported in an economical manner to power plants all over the US.
Coal production in the United States peaked at about 1.2 billion tons in 2008. Since then, the production of coal has slipped significantly as the country sways towards natural gas, renewable and green energies for electricity generation. In 2021, the country managed to produce 577.4 million tons of coal, which is less than half of the amount it produced before.
Aside from coal production, employment in the coal mining business has also dwin dled. Most of the jobs that were cut were in the East. Since 2008, coal mining employ ment fell by:
59% in the East, down from 68,605 workers in 2008 to just 28,314 employ ees in 2021
39% in the West, dropping from 18,114 employees in 2008 to about 11,115 employ ees in 2021
Brief 2021 Highlights of US Coal Performance
In 2021, US coal production went up by 7.8% year over year to 577.4% million short tons or MMst. However, total productive capacity slipped to 871 MMst, a decrease of 6.6% from the previous year's level.
www.skillings.net | 27
Implementing ESG During A Recession
BY MARIE LAGUNA
The mining and metals sector, which was previously demonized in discussions about environmental sustainability, is now recognized as a vital component of the solution. Investors and consumers are becoming more aware of the industry's importance as a supplier of essential raw materials for the global energy transition as well as an important stakeholder in the value chain.
The way mining and metals corporations position themselves in anticipation of the energy transition, especially in light of a
potential recession, will determine their viability and might make or break their competitive edge over the course of the next ten years. Boards should think about how to strengthen current environmental, social, and governance (ESG) frameworks to make sure that they are resilient against the potential economic realities of the future.
To achieve this, it is critical to ensure that ESG is fully included in the long-term busi ness strategy as means of contributing value as opposed to an optional expense to be eliminated.
Evaluating The Resiliency Of ESG In A Recession
ESG is likely to be an important area of concern for stakeholders during a potential recession. ESG investing, according to a recent article in The Economist, "is a dysfunctional system [that] needs urgent repairs." Nevertheless, it aims to hold "firms and their owners accountable for their negative externalities."
high-profile ESG engagement priorities of BlackRock and State Street, along with the more than 5,000 investors who have signed

The
28 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022 SPECIAL FOCUS
As part of the energy transition, mining and metal corporations have started placing a greater emphasis on upgrading their environmental, social, and governance credentials. But will they be able to stick to their promise as a worldwide recession approaches?
the Principles of Responsible Investment, serve as evidence of the depth and breadth of investor commitment in this area. Related proxy voting and activism trends also serve to highlight this commitment.
Risks and opportunities can both be pro duced by ESG variables. For some time now, boards in the mining and metals sector have been working to address a wide range of ESG issues such as how to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and energy use, the working conditions in supply chains, tailings man agement, worker and community health and
safety, and adherence to ever-increasing reporting requirements.
However, during a downturn in the economy, leaders will need to choose which of these themes to emphasize, specify the goals to be met, and outline the anticipated timelines—all against the backdrop of unpredictability in the market and the economy.
Many people continue to believe that choos ing a more sustainable future requires making a trade-off between attaining cor porate growth and profit. They consider
ESG-related expenditures - such as capital costs for energy-use reduction, choosing renewable energy, paying living wages and so on - to be just costs rather than investments.
Companies will face intense pressure to handle ESG factors while maintaining quar terly expectations both before and during any recession. Boards must make sure gover nance standards continue to be in line with market realities because the greater the challenge an executive team has, the more tempting it is to take shortcuts.
Is ESG Mandatory Or Optional In The Mining And Metals Industry?

A rising corpus of research is revealing how important it is to take ESG issues seriously in order to increase resilience, long-term business performance, and investment returns. Businesses with high ESG credentials can outperform their peer groups and the general market.
Mining and metals businesses are investing extensively in efforts to cut emissions or meet other goals in the hopes of seeing a return on their investment in the future. Decarbonization investments, for instance, need high upfront capital expenditures but these might be compensated by tax breaks and enticing financing arrangements. Decar bonization initiatives can also increase energy efficiency which has a direct bearing on operating costs and margins. They also lower the possibility of adverse stock price ramifications or regulatory penalties.
Net-zero targets and the energy transition will fuel demand - and tremendous annual growth in market value - for metals and essential minerals like nickel, lithium, and copper. These factors will also drive demand for energy transition technologies and min erals. ESG drivers - including solid social licenses, appropriate divestitures, and tax transparency - will all be crucial for a com
www.skillings.net | 29
pany's sustained success as the transition to net zero will demand more mining, not less. A worldwide economic downturn could lead to increased cost-cutting initiatives in mining and metals thereby affecting both operations and capital expenditures at a time when further investment commitments are needed to satisfy rising ESG expectations from dif ferent stakeholders. Chief financial officers are under pressure to manage businesses' capital spending plans as they venture into uncharted terrain by allocating funds to initiatives with hefty price tags, protracted timelines, and often elusive returns.
The difficulty of achieving the ideal balance is increased by the fact that businesses fre quently make these investments before new legislation is put forward or before consumer preferences alter. From a financial standpoint,
it involves striking a balance between nec essary spending and possible losses brought on by ignoring or improperly managing ESG aspects. ESG is now the minimum operating standard, particularly in the mining and metals industry. It is no longer optional or a source of differentiation.
It is crucial for the company to align its strat egy to ESG priorities as part of its overall
business strategy through annual reports, proxy statements, sustainability reports, or other public materials after the management determines the appropriate level of corporate investment in ESG.
A Consistent Focus On "E"

Fifty-nine percent of investors, according to the 2022 Accenture Global Institutional Investor Study on ESG in Mining, want miners to pursue decarbonization aggressively and be industry leaders in this endeavor. In the mining and metals sector, almost 63 percent of investors said they would be prepared to sell their holdings in mining companies that fall short of their decarbonization goals or don't undertake enough decarbonization initiatives.
According to this report, mining and metals investors assess "essential" environmental projects as those that reduce scope three emissions, aiming for carbon neutrality by 2050, produce energy-critical metals, and produce no coal. Seven out of ten of the main mining and metals corporations pub licly stated that they wanted to be carbon neutral by 2050.
Other pertinent variables included diver sifying the board, management, and staff; investing in cutting-edge technology and dig italization; and having a great safety record.
By switching from "take, make, and waste" to "take, make, recover, and reuse," core revenue will be improved, and the value of end-of-life materials will be maximized.
SPECIAL FOCUS
30 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022
Risks and opportunities can both be produced by ESG variables. For some time now, boards in the mining and metals sector have been working to address a wide range of ESG issues such as how to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and energy use, the working conditions in supply chains, tailings management, worker and community health and safety, and adherence to ever-increasing reporting requirements.
Recycled resources will go down the cost curve, lowering supply costs and providing insurance against fluctuations in the price of raw materials. Likewise, businesses can leverage their circularity procedures to draw in clients who are concerned about the environment.

Companies are finding it harder to get fund ing if they don't have a systematic plan for closing significant ESG gaps or if they can't demonstrate any real results. This may also make it difficult to enter the stock market, secure licenses or insurance, recruit employ ees, or keep one's social license to operate.
For instance, mine development projects must include ESG and sustainability best practices at every level, from planning to mine decommissioning, as well as through out the supply chain, in order to be bankable. If they are unable to persuade investors that ESG remains a priority, mining and metals companies may also find it difficult to obtain other sources of funding during a crisis.
The Significance Of "G" During A Recession
For succeeding with ESG, solid and creative corporate governance approaches are essential. ESG must be integrated into corporate processes and structures in order to meet set objectives. In this approach, ESG should be viewed as a source of value addition and competitive advantage rather than a risk that needs to be managed or an expense that needs to be cut.
In a downturn, good governance is espe cially important. Alberto Calderon, CEO of AngloGold Ashanti, has declared: "Improv ing operational performance and regaining cost competitiveness against our counter parts provide greater value for us in the medium term."
Focus has shifted from ESG compliance and reporting to stronger commitments with
quantifiable goals and increased reporting openness. Increased regulatory compliance requirements, such as those set forth by the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures, have also played a significant role towards this end.
Additionally, mining and metals corpora tions want to switch their reporting from a broad corporate level to a more detailed mine-site level. According to a Responsible Mining Foundation analysis that examined 38 large-scale mining corporations, few mining companies have truly incorporated the UN Sustainable Development Goals into their business strategy, even though many of them reference them in their sustainability reporting.
Reduced business risks related to an orga nization's ESG footprint might lessen the possibility of regulatory expenses, reputa tional harm, or loss of the social license to operate. The destruction of historic Aboriginal heritage sites in Australia and the deadly dam collapse in Brazil are two examples of how the latter can have a detrimental influence on shared values.
Furthermore, focusing on the "G" and main taining ESG as a top board agenda item,
particularly during a recession, can aid in managing costs, enhancing stakeholder engagement, diversifying supply chains, enhancing performance in comparison to peers, and aiding in the "war for talent" in order to build a sustainable and resilient company. Mining and metals firms can strengthen their balance sheets, experi ence more stable values, and make better long-term investment decisions.
An Essential And Continuous Journey
Inevitably, ESG considerations will alter the business environment for mining and metals industries. A company is unlikely to thrive if it permits itself to become an ESG laggard, especially if peers are setting the bar high.
ESG projects may experience some shortterm erosion during an economic downturn as companies look to cut expenses. Still, over the long run, the focus on ESG concerns will only be revitalized and strengthened. All stakeholders must place their ESG strategies front and center, with the same focus paid to ESG as to the extraction of minerals, if the mining and metals sector hopes to be recognized as a leader in the effort to reach net zero and complete the energy transition.
www.skillings.net | 31
Epiroc Agrees to Acquire Mining Automation Company RCT
BY ROBEL RAMOS
RTC, an Australian company based in Perth, provides an array of automated solutions for either a single machine or an entire mixed fleet of machines. The company offers mining automation and remote-control solutions to the global mining industry.


The acquisition will usher the company to become a “world-leading mining automation solutions provider,” for unloading, loading, and haulage apart from surface and under ground rock drilling.
Currently, RCT has customers in more than 70 countries. The company offers data and information systems, fleet and machine management systems, and machine pro tection systems.
In August 2022, Epiroc announced that they had acquired RNP Mexico. They also said that they would be acquiring mining equipment manufacturer AARD in September 2022.
In a statement, the President and CEO of Epiroc, Helena Hedblom said, “mining auto mation is increasingly important for the mining industry to strengthen safety and productivity, and RCT’s advanced solutions complement Epiroc’s existing automation offering well. Together we will provide com plete mining automation and remote-control
32 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022
Mining expert Epiroc gave the green light to acquire mining automation company Remote Control Technologies Pty Ltd (RCT) and is expected to complete the deal later this year.
MINING TECHNOLOGY
solutions to support our customers on their journey towards optimal operations.” “We are especially pleased that Bob Muirhead, RCT’s founder and a true pioneer within mining automation, will continue in an active management role. We look forward to wel coming the strong RCT team to Epiroc,” the statement stated.
In October 2022, Epiroc launched a new long-hole production drill rig for medium to large-sized drifts designed to provide increased mining automation and high-qual ity drilling. This is the company’s initial step towards its optimization program.
Mikael Larslin, the company’s Global Product Manager of Production Drilling said, “The connected Simba E70 S provides us with performance and quality data, so we can take the first step towards providing tailored process management to our customers.”
Navtech Radar aims to reduce “single point of failure” problem in minining automation
Navtech Radar’s Sam Wood said that banking exclusively on one sensor-based technology for autonomous operations of vehicles is a risk that most mining companies cannot afford to take.
Wood, the Product Manager of Navtech Radar, also said that the issue of operational continuity is likely to become evident in 2026 when an anticipated solar excitation event pushes a lot of GPS-based systems offline. Wood talked to IM on the sidelines of the recent Bauma 2022 fair in Munich, Germany. This event showcased the Amer ican company’s Terran360 single-sensor radar localization solution.
According to Navtech, their machine lever ages the company’s millimeter wave radar technology to reliably position a machine in its surroundings especially in working conditions that are often harsh - like mining and construction. While the Oxford-based
company is well-invested in providing radar-based solutions, the organization is also focusing on integrating its platform into multi-sensor fusion setups at mine locations thereby integrating with LiDAR GPS and others.
“We see our solutions complementing and integrating with other technologies,” Wood said. “We feel mines and other industrial sites should not have a ‘single point of failure’ within an automated setup as this can lead to unnecessary downtime, or – in some cases – potential accidents or injuries.”
A spike in GPS attacks, by “jamming” or “spoofing”, effectively means that depending completely on GPS is turning into a commer cially risky proposition for autonomous mine operators. “Terran360, and other examples of innovation developed by Navtech, aims to address these challenges,” Wood said.
The President and CEO of Epiroc, Helena Hedblom said, “Mining automation is increasingly important for the mining industry to strengthen safety and produc tivity, and RCT’s advanced solu tions complement Epiroc’s existing automation offering well.
In partnership with Oxbotica, an autonomous software expert, the Terran360 is certified to IP66 standard. The radar localization technology installed is protected from water and debris. This ensures constant operations with minimal maintenance to allow 100% visibility of assets at all times. “Oxbotica’s world-class localisation algorithms are com bined with Navtech’s ruggedised industrial radar sensors to provide a package that is resilient to weather and harsh environments,” Navtech added.
Oxbotica’s product portfolio in the mining industry includes software for the entire technological spectrum from low-level sensor managers to calibration, four-modal localization, mapping, perception, 3D map ping, and planning and control.
Navtech added, “In the mining and con struction industry, autonomous vehicles solely depend on GPS sensors to report their whereabouts. However, their ability to reliably maintain centimeter-level posi tioning required for autonomy, particularly within developments with tall infrastruc ture, deep pits, or at high latitudes, is often compromised.
“Terran360, on the other hand, draws on high-resolution radar technology which penetrates the atmospheric and weather conditions to constantly deliver highly accu rate, centimeter-level location data,” Navtech further explained.
The two companies have been partnering on solutions for the industry after several successful radar deployments. Amongst them are the trials in one of Boliden’s major underground mines in Europe wherein the radar sensor provided situational awareness to support machine retrieval from smokefilled mining tunnels.
Navtech has also partnered with Örebro University in Sweden where its radar-based sensor was tested as part of a sensor fusion project with the school’s Centre for Applied Autonomous Sensor Systems. This trial has seen the company’s teleremote and auto mated setup in applications like mining. Wood also said that more companies are keeping their eyes on these kinds of automated solutions. Navtech also sees demand for radar-based platforms in other applications.
www.skillings.net | 33
World’s First Hydrogen-Powered Haul Truck Could Contribute To A Cleaner Mining Industry
a Typical mining haul Truck is one of The largesT vehicles on the planet - standing three stories tall and weighing 500 metric tons when fully loaded. It also happens to be a major contributor to emis sions in an industry which is often accused of polluting.
BY MARIE LAGUNA
According to the consulting firm McKinsey, the mining industry contributes up to 7% of global carbon emissions each year. According to David Gerhardt, principal systems engi neer for First Mode, a Seattle-based clean energy company, roughly 50% of this comes from haulage trucks which are used to trans port heavy rocks between different sites.
That is why First Mode is developing a zero-emission alternative to the truck's diesel engine. To do so, it is turning to one of the world's most abundant natural resources: hydrogen.
After launching the project in 2019, the company claims to have built the world's largest mobile hydrogen power plant - a hybrid that combines hydrogen fuel cells with battery power. The power plant must generate two megawatts of electricity per second in order to power a vehicle of this size, which is enough energy to power 1,500 American homes.
Creating Mining Moves
Gerhardt claims that in order to meet that output target, they had to do something never done before. "The scale of fuel cells that we needed did not exist on the market," he says. Instead, First Mode combined several smaller fuel modules to create a 25-metricton hybrid power plant.
Gerhardt describes the power plant as weighing five elephants and capable of carrying a load weighing 100 elephants. "Imagine the force required to move 100 elephants up the hill at 15 kilometres per hour," he adds.
The hydrogen-powered haul truck made its official debut this past May, three years after the project began, at Anglo American's Mogalakwena mine in South Africa.

According to the mining multinational that commissioned the development of First Mode's power plant, an average mining haul truck in its fleet consumes 900,000 litres
of diesel fuel per year. While hydrogen fuel cell vehicles have been around since the 1960s, their adoption in the mining industry is relatively new, with many companies only now beginning to set emissions reduction targets. Prior to First Mode's truck, the only other zero-emission vehicle of this scale was a Swiss all-electric mining haul truck.
According to Chris Voorhees, CEO of First Mode, partnering with Anglo American "has provided us with a platform and an
34 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022 MINING EQUIPMENT
entry point into what is a very complicated environment, which is the mine operation itself." However, according to Voorhees, the decarbonization of the industry extends beyond haul trucks to how raw materials are sourced, created, and manufactured.
As per the First Mode, the newly announced agreement will sharpen the focus on decar bonizing global mining operations and developing clean technology solutions for the world's largest industrial applications.
"The investment supports First Mode's capac ity for growth, scaling to meet customer needs for clean energy across many indus tries, and investing in their most important product: their people."
As of the end of last year, First Mode had 75 employees, three of whom were based in Perth, Western Australia, which is a mining hub. Those numbers have grown significantly since then, with First Mode now employing more than 100 people, including approxi
mately 18 in Australia. Anglo American's investment was announced in the form of a Form D filing with the Securities and Exchange Commission. According to the filing, First Mode was raising $32.5 million in funding, with $8.5 million in equity sold.

The Power Potential Of Hydrogen
More industries, ranging from ground transportation to aviation, have recently turned to hydrogen as an energy source. Germany unveiled 14 hydrogen-powered passenger trains in August. Airbus has also stated that it intends to test hydrogenpowered planes in 2026.
Glenn Rambach, an energy research engineer who has worked in the field for over four decades, believes hydrogen technology will eventually outperform electric batteries.
However, he adds that one of the primary challenges facing a project of this scope is sourcing and producing the type of hydrogen fuel required to support a fleet of haul trucks.
Rambach believes hybrid vehicles, which are powered by a combination of hydrogen and electric batteries, are best for powering heavy-duty vehicles and can "soften the challenge of any inadequacy in electricity or hydrogen infrastructure."
However, the carbon emissions from using hydrogen as a fuel are determined by how the hydrogen is produced. Green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources, whereas blue hydrogen is produced using fossil fuels. Green hydrogen detractors argue that using renewables to create another fuel is a waste of clean energy.
As per the First Mode, its hauling truck was designed to run on green hydrogen, and the company is working to develop a sustainable supply chain to support the trucks.
www.skillings.net | 35
The nuGenTM truck is retrofitted from a diesel-powered vehicle. | © Photo: Anglo American
Angola Set To Become Globally Competitive Mineral Producer
in recenT years, angola has Tapped inTo iTs rich mineral wealTh in several ways in order To diversify its economy. In an article for Energy Capital & Power, Miguel Artacho stated that Angola is the leading producer of crude oil in sub-Saharan Africa. In the third quarter of 2021, the country’s mining sector contributed to 1.6% of its GDP - primarily through the export of diamonds. Surprisingly, the country is the sixth-largest producer of diamonds globally despite the fact that it has only exploited about 40% of its reserves.
BY JOHN EDWARD
The global energy transition and the use of strategic minerals in lithium-ion batteries are expected to dramatically increase the demand for rare-earth elements. The mining industry is cognizant of these developments and is expected to play a bigger role than ever before in contributing to Angola’s GDP. Indeed, several key developments across the mining and extractive industries were in the spotlight as Angola celebrated the 37th anniversary of its Mining Labor Day in April 2022. Some of these are highlighted below:
Diamond Production
According to H.E. Diamantino AzevedoAngola’s Minister of Mineral Resources, Petroleum and Gas - the country is on the road to becoming the second-largest producer of rough diamonds globally by 2030. The growth is linked to developments across the diamond space coupled with market-driven regulatory reforms that have enabled investment in the sector.
These reforms include the establishment of the National Agency of Oil, Gas and Bio fuels as the national concessionaire along
with the approval and implementation of Presidential Decree 143/20. The latter is a governance model which has streamlined the mining sector by reducing the State’s role. A significant boost has also come from measures that promote transparency along with fiscal incentives for encouraging the exploration of mineral wealth.
Currently, Angola is the fourth-largest pro ducer of diamonds globally - with production estimated to be around 9.3 million carats in 2021. However, about 60% of the country’s mineral basins remain unexplored which

SPECIAL FOCUS
36 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022
opens up crucial opportunities for further exploration. It comes as no surprise then that Angola is accelerating diamond mining activities in 2022 and beyond.
Retaining Value In The Country
Angola has been focusing on building capacity in the domestic mining sector in order to galvanize its economic and industrial development. The country has ramped up local production and manufacturing industries to stimulate job creation, industrialization and infrastructure development.
Angola has invested in a slew of for ward-looking initiatives. For instance, given the fact that the country currently exports 95.5% of its rough diamonds, the Ministry announced plans to cut 20% of diamonds domestically in April 2021.
The country also launched the $77-million Saurimo Diamond Development Hub in August 2021. This facility brings the entire diamond value chain together and consists of three major diamond cutting factories along with a diamond cutting and polishing training center to facilitate capacity build ing and skill transfer. Similarly, Angola has heavily invested in upskilling its local mining workforce – a development which the country celebrated during Mining Labor Day 2022. An initiative of the then-Defense and Security Council, Mining Labor Day is a celebration of the role that mining workers play in transforming Angola’s mining sector and the fabric of the national economy.
Riding The Strategic Minerals Wave
Apart from diamonds, Angola is blessed with iron ore, phosphates, copper, gold and manganese. There are 28 gold mining projects - including 20 in the prospecting phase - with average production capacity for each mine pegged at roughly 4.5 kg per month. However, it might just be the
country’s energy transition-related minerals which rope in foreign investment.
With shifting global priorities and new technologies like electric vehicles (EV) and battery storage, rare-earth elements found on the African continent have become hot commodities. Estimates by The World Bank predict that mineral production is likely to increase almost five-fold by 2050. Further more, roughly 3 billion tons of minerals and metals will be needed to sustain wind, solar and geothermal power expansion along with energy storage.

Consequently, the demand for minerals like lithium, nickel, copper, cobalt, man ganese and graphite has escalated. These minerals are essential for battery perfor mance. Similarly, the demand for minerals like neodymium and praseodymium (NdPr)
has increased dramatically because of their utilization in wind turbines and EV pro duction. Angola has taken action to ensure that it is at the cutting edge of producing energy-transition minerals at the global level. For instance, the Longonjo Rare Earth Project is set to become the first major rare earth mine in Africa.
The project is located near the city of Huambo and has a production target of 56,000 tons per year. The initiative will be operated and funded by London-listed Pensana Plc along with additional funds coming from Angolan Sovereign Wealth Fund (FSDEA).
The country has also positioned itself stra tegically to meet the surge of demand in clean energy by targeting investment and development within the sector.
www.skillings.net | 37
Smart Technology Drives Promising Market Growth for Global Mining Automation
arTificial inTelligence, augmenTed realiTy, and remoTe conTrol solutions are starting to emerge as major market drivers of mining automation industries. Previous forecasts from Zion Market Research revealed that the global market size of mining automation will increase by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% until the year 2030.
BY RANDY MOLEJONA JR.
Part of the catalysts for this rapid market growth is the array of technological advancements initiated around the globe to conserve energy, increase productivity, and promote safety in harsh mining environments.
The call for these innovations in mining auto mation comes from the escalating demand of the industrial sector for common base metals, thereby pushing the development of high-productivity technologies for mining exploration activities.
One of the technological trends attract ing investments in the mining automation industry is the development of autonomous surveying technology through artificial intel ligence (AI).
“The integration of autonomous surveying technology into a construction workflow has groundbreaking potential,” said Aviad Alma gor, Vice President of Technology Innovation of Trimble, after the announcement of his company’s partnership with Exyn Technol ogies in Nevada, USA in November 2022.
The Trimble X7 already has high accuracy and speed when it comes to capturing the surrounding environment through 3D laser
scanning. However, a brand-new potential can still be unleashed with the integration of smart technology from the autonomous robots powered by ExynAI. These robots are equipped with sensors to avoid obstacles regardless of the complexity of the construc tion environment. Self-navigation without the need for a GPS is also one of the emphasized features of this innovation.
Another emerging development derived from augmented reality (AR) is being launched by Torsa in Antamina, Peru. The Collision Avoidance System (CAS) features centi metric precision for detecting hazards in the vehicle’s surroundings to improve the safety of the operator while fetching realtime data that could be useful for remote management centers to optimize current mining operations.
“In our fourth generation CAS system, we have incorporated a predictive algorithm to avoid false positives, because we know that this is key for someone who is driving many hours every single day,” explained Gabino de Diego, the new Business Development Director of Torsa. He also acknowledged the help of business intelligence modules which allowed users to replay footage of incidents to serve as a reliable basis for generating corrective measures.
Remote control solutions are also seen to influence major business decisions as the mining specialist, Epiroc, gains control over Remote Control Technology (RCT) company in October 2022. This smart technology com pany based in Perth, Australia is expected to serve as a vital player in Epiroc’s goal to become one of the leading automation solutions providers around the world.
Helena Hedblom, CEO and President of Epiroc, welcomed Bob Muirhead, founder of RCT, as she announced that the latter will remain in an active management role upon joining her team. One of the expected contributions of RCT is to provide auto mation on either a single or mixed fleet of machines, regardless of manufacturer and type of equipment, effectively maximizing compatibility. However, the rise of these innovations comes with significant envi ronmental responsibility. Fortunately, green initiatives are extensively discussed during the development of these mining automation technologies.
In November 2022, Epiroc introduced the Smart and Green Series to highlight the company’s efforts in designing zero-emission vehicles without compromising productivity. As tested, these battery-electric vehicles showed positive results in reducing carbon emissions, improving sustainability, and satisfying end-users.
Two of the sustainability-centered compo nents of the Smart and Green Series is the use of fossil-free steel sourced from SSAB and green batteries developed from North volt. The materials of the mining equipment used in the series were claimed to, indeed, reduce carbon dioxide and other green house gas emissions. On the other hand, the high-energy density batteries used for the machine models were said to be certified to comply with international standards and designed with multiple safety features.
With all the mentioned progress, one of the
MINING TECHNOLOGY
38 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022


www.skillings.net | 39 Name Company Address .........................................................Suite... City:..............................State:..........................Zip:.............................. Phone ............................. Fax .............................................................. E-Mail MINING INFO YOU DON’T HAVE TO DIG FOR... SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW. P.O. 1203 NOKOMIS, FLORIDA 34274 Subscription Information TEL: 888-444-7854 X 4 | FX: 888 261 6014 subscriptions@skillings.net SUBSCRIBE NOW FOR IRON ORE MINING NEWS AND MORE... Check your choice of Subscription Skillings Mining Review Print Subscriptions United Stages Mainland a Print Monthly Magazine Skillings Mining Review - Mail Delivered a Digital Subscription One-Month c $72 12 Months c $800 Skillings Mining Review Print Subscriptions Global a Print Monthly Magazine Skillings Mining ReviewMail Delivered a Digital Subscription One-Month c $250 12 Months c $2950 Skillings NewsRoom Digital Subscription a 3x Weekly Digital Newsletters: The Americas, Global and Equipment a Video News Updates a Digital Monthly Magazine Skillings Mining Review e-mailed a Website Full Access Skillings.net Podcast | Videos One-Month c $4.95 12 Months c $55.00 12 Months c $660.95* *Group License (Unlimited Access Company wide) c Amount Enclosed c Please Bill Me Card Number: Exp. Date: c Visa c Master Card c American Express CVS No. (Security Code):
2022 ANNUAL INDEX
OF SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW
Perusing through our 100+ annual index will give the reader a good retrospective of 2022. New headings reflect trends unique to what has been an extremely interesting year. There is an increasing emphasis on sustainability - clean technologies, waste water management, re-vegetation and adherence to legislation.
SPECIAL FOCUS
Article Month P
Times Of Economic Complexity, Going for Gold: An Idea Jan 34
Advantages of Growing Renewables on Contaminated Lands Jan 36
Miners Alert: Global Push For Green Steel In Way Of $150 Billion In Iron Ore For Australia: Adapt Says Analysts Jan 43
Philippines Mining Industry Reviving After the Shock Feb 18
Underground Mining Market To Go Upto US$ 25 Bn By 2031: Comprehensive Inspection Solutions for Mining Giants Behind the Revenue Gains
Feb 38
SPECIAL FOCUS
Article Month P
Plans Keep ON for Wind Turbines
Mar 20
Western Blazes: Are Underground Coal Fires Responsible! Mar 40
$144 Million Given by Biden-Harris: Paving Good-Paying Union Salaries: Reviving Coal Groups April 18
Epanko Graphite Project in Tanzania: EcoGraf Chooses Vermeer as a New Companion to Assess Surface Mining Technology April 22
Russian Ukraine War Impacts Mining Supply Chains April 24
The State of Precious Metals Feb 42
Hamilton Harbor Lighthouse: Allow Public Access Soon Mar 16
Iron Ore Price Up as a Consequence of the Russia- Ukraine Conflict April 26
Russia-Ukraine War at Play Ferrexpo Share Drops by 70% April 27
40 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022
SPECIAL FOCUS
Article Month P
Thousands of Roles, No Experience, Easy Entry: Australians can now earn more than $160,000 a year April 28
Stabilize Prices in China: Supporting Iron Ore Market Management April 20
Iron Ore Miners Revitalizing April 42
On Earth and Beyond Now, from Ancient Pro fession to Modern Mining May 22
AMC has a Gold Mine! May 38
Former Rio Tinto Executive for Uranium Mine Leadership: Environmentalists’ Criticize and Concern May 43
Bipartisan Infrastructure Law Boosts in house battery production with $3.16 Billion June 18
Circular Thinking: The Key to Sustainable Mining in Africa June 26
Best Dividend Paying Mining Metal Stocks June 40
Geotechnical Software, Finally a dry solution July 38
China Recovers Iron Ore on the High July 26 Engineering Projects of the Coming Age, What a Transformation! July 28
Environmental harm from mining emissions is estimated to be worth £2.5 trillion annually Aug 26
The Pilbara’s most technologically advanced mine is Gudai-by Darri’s Rio Tinto Aug 38
Global Opportunities and Demand by Top Play ers in the connected mining market Aug 40
China No More Dependent Upon For eign Iron Ore Sep 26
Resuming the Cut Task: Woodsmith Shaft Boring Roadheaders Sep 36
Prevention is the Predictive Cure! bulk han dling in mining Sep 38
Mining Technology Inculcation: Australia a Trendsetter! Oct 16
SPECIAL FOCUS
Article Month P
Grängesberg Iron Ore, Dalarna County, Sweden Resuming Oct 29
Audit: Intelligent Unmanned Mining Oct 36
Latest Uranium/Vanadium district: Advanced exploration: Argentina Nov 26 Lithium Mining in North America Nov 30 Coal Companies Recklessly Going Go! Nov 38 Fogmaker south africa: Dominate ema 2022 show: With Smart, Efficient And Cost-Effective Fire-Suppression Practices Nov 42
Is It Possible For The Iron Ore Mining Industry To Go Green? Nov 44
THE LEAD
Article Month P Why Women are Quitting the Mining Industry and what mining companies can do about it Jan 8
The Best Copper Stocks potential in 2022 Feb 10 Environmental Loses Due to Unethical Sand Mining! Mar 10
Discover the Largest Critical Mineral Mines of America April 10
Oklahoma Report: Climate Change Plays Chaos With Mining Education May 10
The Salton Sea would produce the world’s Greenest Lithium let the latest extraction tech nologies work! June 10
Rio Tinto: The Ultimate Commodity Leader for Commodity Expansion July 8
Iron Hunt in China Aug 8
Biden All Set To Promote Minerals, However, Lag In Mine Permits Sep 8
Australia: Brightening Up as the Latest Rare Earth Elements Producer Oct 8
www.skillings.net | 41
THE LEAD
Article Month P
Sandvik Needs To Be Applauded In Under ground Mining: Established A New and Commendable Battery System Safety Standard Nov 8
PROFILES IN MINING
Article Month P
Interview with Heng Huang, Financer, HOT Mining Tech Co., Ltd, Beijing. Jan 28
Interview with Mr. Marc Mesa Capodicasa. Founder & CEO, Eco–Soil Group Feb 30
Interview with Mario Santiago Juarez, 1st Member, Senior Mine Engineer, CADIM. www. terraomnia.ar Mar 30
Interview with Joseph Sam, Chief Business Office. Exclusive Quarries P Limited April 30
Interview with Ta M. Li, Retired Vice President, Operations, Tetra Tech May 30
Interview with Scott Austin Quillinan, Senior Director of Research, University of Wyoming School of Energy Resources, USA. June 32
Interview with Mr. Ludovic Donati. Group Chief Digital Officer, Eramet July 30
Interview with Mr. Phil Christopherson. CEO, Energy Capital Economic Development Aug 30
Interview with Mr. Prasanajit Mishra, Founder and Managing Director, Mining Today Sep 32
Interview with Trina Igelsrud Pfeiffer, Interim Director, Center for Carbon Capture and Con version, at the University of Wyoming Oct 32
Deep-sea Mining: Environmental And Social Considerations And Risks. By Tom Mills, Founder & Managing Director of Two Oceans Strategy, London, UK.
STATISTICS
STATISTICS
Article Month P
Crude steel production December 2020 Mar 47 February 2022 crude steel production April 46
Crude steel production December 2020 April 47 March 2022 crude steel production May 46
Crude steel production December 2020 May 47 April 2022 crude steel production June 46
Crude steel production December 2020 June 47
May 2022 crude steel production July 46
Crude steel production December 2020 July 47 June 2022 crude steel production Aug 46
Crude steel production December 2020 Aug 47 July 2022 crude steel production Sep 46
Crude steel production December 2020 Sep 4 7
Great Lakes Iron Ore Trade Down in August Oct 26 August 2022 crude steel production Oct 46
Crude steel production December 2020 Oct 47 August 2022 crude steel production Nov 46 Crude steel production Nov 47
SURFACE MINING
Article Month P
How can we ensure that technology is adopted in the mining industry?
Nov 32
Article Month P
November 2021 crude steel production Jan 46
Crude steel production December 2020 Jan 47
November 2021 crude steel production Feb 46
Crude steel production December 2020 Feb 47
December 2021 crude steel production Mar 46
Jan 20
In 2031, the global smart mining market is expected to reach US$55.15 billion Jan 22
In a bid to boost iron-ore rebound, Vale has lowered its production guidance Jan 25 Mining diplomacy’ is critical for the future of energy Jan 26
Australian Mining Companies Try to Scrap Old Equipment
Billion-Dollar Lithium Drilling Project Aims U.S. to Energy Independence
Surge Battery Metals: Northern Nevada: First Outcomes of the Lithium Exploration Programs
Feb 8
Feb 16
Feb 24
Blueprint Ready for Commercial Mine Energy Storage Capacity in Sweden Mar 24
Honduras Stops Open-Pit Mining
April 6 42 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022 ANNUAL INDEX
SURFACE MINING
Article Month P
Mining Jobs In India May 25
Kamoa Copper to enlarge by the concentrator June 24
Vale Hits a Nickel Supply Deal with Tesla: Ensures Long-Term Collaboration June 24
Palito output has ‘continued to improve,’ accord ing to Serabi Gold July 05
Iron Ore Revival July 06
Nucor Expanding ON Steel Utility Structures: Acquires Manufacturers July 06
Michael C. Liptak, Co-Founder of ALL, Dies at 91 July 16
CR Meyer Announces Leadership Suc cession Plan July 17
In April through June, Vedanta’s aluminium production increased by 3% to 565,000 tonnes Aug 05
CGG Advances on Geothermal Resources R&D Aug 21
At MIT, an old African smelting method is being revived Aug 22
ASV RT-50: Yanmar-Powered with More Power and Comfort Aug 25
Sepro gets the award for water conservation technology Aug 42
McFarlane Lake Completes some Handsome Acquisitions Sep 05
Ollagüe Salar: Strategic Partnership Sep 06
Magnus Mineral Resources and Sixth Wave Innovations sign MoU Sep 14
Latest on Ojos del Salado in Chile Sep 16
The Impact of China Steel Mills on Iron Ore Prices Sep 16
India: Bellary Reddy Mining, Andhra ‘No Objection’ Sep 22
U.S. Representative Mike Gallagher 2022 Leg islator of the Year Sep 29
Exciting Lithium Projects in Canada Sep 44
Agnico Eagle’s Fosterville Gold Mine: Big Preparations Oct 05
Iron-Ore Processing: New Gen Compact Pelletizing Oct 06
Mantos Blancos and Manotverde mines in Chile Oct 06
Metso Outotec Expands: Pennsylvania Oct 06
SURFACE MINING
Article Month P
Shaft sinking innovations, safer work place by 2040 Oct 15
Slam Exploration Mobilizing to Drill Gold Veins at Menneval Oct 19
Vale Unveils the Next Sustainable Sand Operation Oct 31 Gold Mining Stocks Bullish Mid October Nov 21 John Robins Joins Gelum Resources as Advisor Nov 22
Fossil Fuel Growth Vs. Clean Energy’s Progress Nov 24 2022 Great Lakes Marine Hall of Fame Inductees Nov 29
UNDERGROUND MINING
Article Month P
Hanstone Gold appoints a Director, Chief Financial Officer, and Executive Chairman
At Its Spanish Mountain West Project, West Mining Identifies Several Geochemical Anomalies. Bc
Critical Minerals Could Be A Threat To America’s Security. Mineworkers, on the other hand, are in short supply.
Greatland Gold Gives Out Proceedings of the Juri JV final Exploration
Fifty-nine people killed in Burkina Faso Gold Mine blast
Jan 05
Jan 06
Jan 24
Feb 28
Mar 05
Largest Coal Project In India, More Jobs Promised Mar 27
The State of North Dakota has been awarded $2.8 Million to Reclaim and Repurpose Abandoned Coal Mines
Report World Bank Group: “Minerals for Climate Action.”
April 05
April 08
Advisory Appointment for Quim baya Gold Inc. May 05
Anne Currie appointed to the FPX Nickel Board of Directors May 06
Lithium reserves in India and the game-changing Australian lithium partnership
May 06
SME Statement: Domestic Mining Education Act of 2022 May 08
www.skillings.net | 43
UNDERGROUND MINING
Article Month P
With Rio’s bid, Turquoise Hill Stockholders Might Make Lots of Profits
May 26
Nickel Price Spike could Pull the IGO’s Western Area Deal into Shreds May 28
Artisanal mine: 35 Killed in a Raid June 22
Labrador West Iron Project Gets a Start: High Tide Begins Drilling June 22
Expanded state mining rights not okay in Chile’s constitutional assembly June 25
Rio Tinto: Reviving the Serbian lith ium project June 29
Elon Musk’s Supply Chain All Set To Change the Energy Sector June 30
Mining Equipment Industry Up To $133.2 Billion: 2026 Forecast July 18
Wicheeda Rare Earth Element Deposit Pit Slope July 19
Geotechnical Services in Northeast Flor ida Boosted July 20
UES Equipped with a $5M Contract by Flor ida Department of Transportation July 20
Mining industries in India: India wants to take its metal-based industries to the next level
July 22
National award for Baltimore emergency repair project: EBA Engineering July 37
USA Rare Earth, Gov’t to Bolster Domestic Mineral, EV Battery Supplies
July 42
Tennessee Valley Authority completes Boone Dam remediation project July 44
Worley purchases Minera Mining Technolo gies, an automation expert
Uplifting Ore Processing in this Century
Up, Up, Down, Down Uranium. Only ura nium is the winner!
Aug 06
Aug 06
Aug 20
$4,000,000 Strategic Investment: Labra dor Iron Mine Aug 24
Foley Mine Area Soil Geochemical Program Completed by Q-Gold Sep 06
Clean TeQ Water shares rise, Dewatering Technology Sep 18
UNDERGROUND MINING
Article Month P
Latest Geopolitical Tensions Improved Gold Performance Sep 20
Simandou: China’s Latest Iron Ore Supplier Sep 30
India: Sandvik Mining Automation Learning Center Opened
Viscount Mining TITAN MT Survey Confirms Conductive Anomaly at Silver Cliff, Colorado
Oct 14
Oct 20
Iron & Steel: The Route Starts! Oct 39
Oct 40
Awards Ceremony Recognition: Long wall Automation from Anglo American’s Milestones
Phase III RC Drilling Results Confirm South ern Extension of Christmas Gift Prospect Burracoppin Gold Project, WA
Oct 44
SolGold & Cornerstone Merger Transaction Nov 25 CGG Awarded Critical mineral exploration Study in Argentina Nov 41
MINING INSIDER
Article Month P
Tesla Supply Deal Leads to Talon Stocks Expe riencing a Peak
Feb 05
Bam Bam BOD: Now Accomplished with a Professional Geologist Feb 23
ALLETE Senior VP and CFO Robert Adams announces retirement plans
Feb 29 Pedestrian Bridge Over Shoreway: On the Go Feb 08
Signal Peak Energy was fined $1 M for safety, and pollution violations
Talon is part of the Battery Materials and Tech nology Coalition
SHIPPING
Feb 18
Feb 44
Article Month P
The Final Laker Arrives! March 06 More on the Great Lakes: Winter Begins Officially March 38
Shipping Rebound for Great Lakes, Covid Turns Down March 28
44 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022 ANNUAL INDEX
RARE EARTH





Azcon 45 ABT 21 Barr Engineering 15 CR Meyer 23 FloLevel Technologies ................. 25 Fryberger....................................... 15 General Equipment Supplies ....... 05 Global Minerals Engineering ....... 45 Golder Associates ........................ 45 Halcor ........................................... 13 Lake Superior Chapter ISEE ......... 45 Malton Electric Company ............ 45 ME Elecmetal ............................... 07 Minnesota Power ......................... 17 Mielke Electric Works .................. 17 Naylor Pipe ................................... 48 Neo Solutions ............................... 19 Northern Engine & Supply ............ 45 Optiro ............................................ 02 SEH ............................................... 21
INDEX golder.com We thrive on challenges
ADVERTISING
A Bundle of Fresh Mining Jobs in Saudi Arabia: 14500 in Planning June 28 Job Growth in Coal Counties: VTS Tar gets Confirmed Nov 20 Shale drillers Struggle for Workforce Nov 22
EQUIPMENT Article Month P Novel Self-Propelled Bale Chaser: Con tractor Work Oct 22 Mineral Management Software Suite Nov 37 Slam Exploration Mobilizing to Drill Gold Veins at Menneval Nov 41
MINING JOBS
MINING
Article Month P NioCorp CEO: Do Not Count On China For Rare Earth Metals Nov 18 www.skillings.net | 45
october 2022 crude steel production
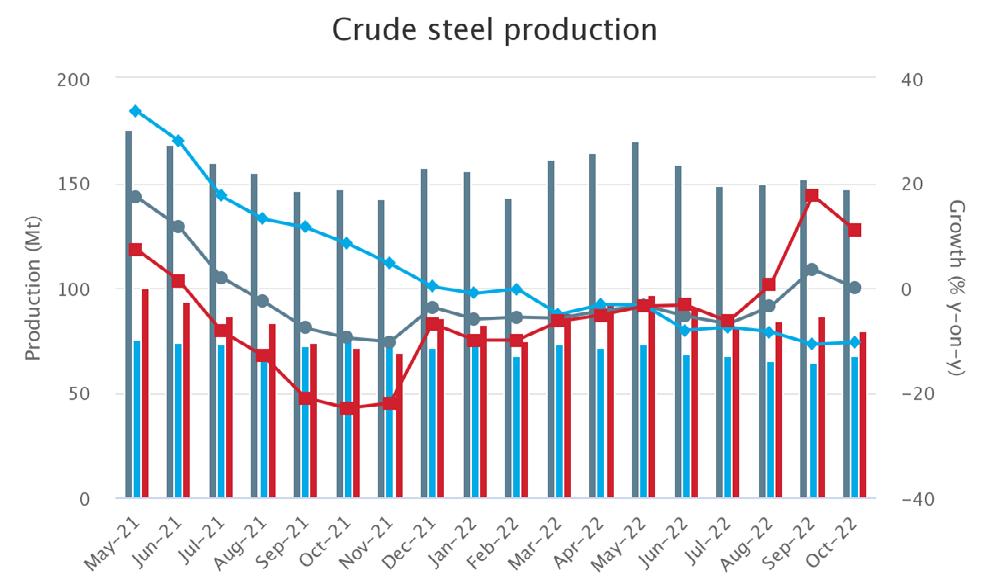
World crude steel production for the 64 countries reporting to the World Steel Association (worldsteel) was 147.3 million tonnes (Mt) in October 2022, a 0.0% change compared to October 2021.
CRUDE STEEL PRODUCTION BY REGION
Africa produced 1.4 Mt in October 2022, up 2.3% on October 2021. Asia and Oceania produced 107.3 Mt, up 5.8%. The EU (27) produced 11.3 Mt, down 17.5%. Europe, Other produced 3.7 Mt, down 15.8%. The Middle East produced 4.0 Mt, up 6.7%. North America produced 9.2 Mt, down 7.7%. Russia & other CIS + Ukraine produced 6.7 Mt, down 23.7%. South America produced 3.7 Mt, down 3.2%. The 64 countries included in this table accounted for approximately 98% of total world crude steel production in 2021. Regions covered by the table: Africa, Asia and Oceania, European Union (27), Europe, Middle East, North America, Russia & other CIS + Ukraine, South America.
Table 1. Crude steel production by region
TOP 10 STEEL-PRODUCING COUNTRIES
China produced 79.8 Mt in October 2022, up 11.0% on October 2021. India produced 10.5 Mt, up 2.7%. Japan produced 7.3 Mt, down 10.6%. The United States produced 6.7 Mt, down 8.9%. Russia is estimated to
have produced 5.8 Mt, down 11.5%. South Korea produced 5.1 Mt, down 12.1%. Germany produced 3.1 Mt, down 14.4%. Türkiye produced 2.9 Mt, down 17.8%. Brazil is estimated to have produced 2.8 Mt, down 4.5%. Iran produced 2.9 Mt, up 3.5%.
Table 2. Top 10 steel-producing countries
oct 2022 (mt) % change oct 22/21 jan-oct 2021 (mt) % change jan-oct 22/22 africa 1.4 2.3 12.5 -5.6 asia and oceania 107.3 5.8 1,145.3 -2.1 eu (27) 11.3 -17.5 117.1 -9.2 europe, other 3.7 -15.8 38.4 -9.8 middle east 4.0 6.7 36.4 7.7 north america 9.2 -7.7 94.0 -4.7 russia & cis + ukraine 6.7 -23.7 72.6 -19.0 south america 3.7 -3.2 36.4 -4.5 total 64 countries 147.3 0.0 1,552.7 -3.9
oct 2022 (mt) % change oct 22/21 jan-oct 22 (mt) % change jan-oct 22/21 china 79.8 11.0 860.6 -2.2 india 10.5 2.7 103.8 6.1 japan 7.3 -10.6 75.2 -6.5 united states 6.7 -8.9 68.1 -4.8 russia e 5.8 -11.5 60.4 -6.6 south korea 5.1 -12.1 55.7 -5.0 germany 3.1 -14.4 31.4 -6.9 turkey 2.9 -17.8 30.2 -10.1 brazil e 2.8 -4.5 28.7 -5.2 iran 2.9 3.5 25.1 9.0
The 64 countries included in this table accounted for approximately 98% of total world crude steel production in 2020. Regions and countries covered by the table: Africa: Egypt, Libya, South Africa. Asia and Oceania: Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Pakistan, South Korea, Taiwan (China), Vietnam. CIS: Belarus, Kazakhstan, Moldova, Russia, Ukraine, Uzbekistan. European Union (27). Europe, Other: Bosnia-Herzegovina, Macedonia, Norway, Serbia, Turkey, United Kingdom. Middle East: Iran, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates. North America: Canada, Cuba, El Salvador, Guatemala, Mexico, United States. South America: Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru, Uruguay, Venezuela
STATISTICS
46 | SKILLINGS MINING REVIEW December 2022
COUNTRY
CRUDE STEEL PRODUCTION DECEMBER 2020. Source – World Steel
DEC 2020 DEC 2019 %CHANGE DEC-20/19 2020 % CHANGE
Austria 530 e 521 1.7 6 665 -10.2
Belgium 359 505 -28.9 6 119 -21.1
Bulgaria 40 e 43 -6.3 485 -14.3
Croatia 15 e 7 101.9 47 -32.0
Czech Republic 408 359 13.7 4 465 0.6
Finland 339 186 81.8 3 500 0.8
France 1 155 918 25.7 11 596 -19.8
Germany 3 137 2 835 10.6 35 658 -10.0
Greece 110 e 94 17.0 1 430 5.9
Hungary 90 164 -44.8 1 513 -14.5
Italy 1 500 e 1 404 6.9 20 200 -12.9
Luxembourg 113 97 17.3 1 886 -11.0
Netherlands 540 521 3.6 6 054 -9.1
Poland 680 e 642 5.9 7 890 -11.9
Slovenia 50 e 34 45.0 570 -8.5 Spain 891 765 16.4 10 934 -19.5 Sweden 410 376 8.9 4 409 -6.6
United Kingdom 710 e 550 29.0 7 185 -0.5
Other E.U. (28) (e) 680 e 642 6.0 8 180 -12.1
European Union (28) 11 757 10 665 10.2 138 786 -11.8
Bosnia-Herzegovina 75 70 6.5 759 -5.2
Macedonia 33 24 35.9 180 -24.8 Norway 41 40 3.2 624 0.5 Serbia 119 158 -24.8 1 456 -24.6 Turkey 3 403 2 893 17.7 35 763 6.0 Other Europe 3 671 3 185 15.3 38 782 3.9
Byelorussia 200 e 225 -11.2 2 490 -5.0 Kazakhstan 355 e 374 -5.0 3 835 -7.2
Moldova 45 e 35 28.2 465 18.7
Russia 6 110 e 6 159 -0.8 73 400 2.6 Ukraine 1 906 1 561 22.1 20 616 -1.1 Uzbekistan 80 e 84 -4.8 950 42.6 C.I.S. (6) 8 696 8 438 3.1 101 756 1.5 Canada 1 070 e 1 092 -2.0 11 078 -14.1
Cuba 20 e 22 -8.5 181 -21.4 El Salvador 8 e 8 -5.7 79 -22.5 Guatemala 25 e 26 -3.9 237 -22.6
COUNTRY
Mexico
Association
DEC 2020 DEC 2019 %CHANGE DEC-20/19 2020 % CHANGE
1 550 e 1 361 13.9 16 854 -8.3
United States 6 434 7 292 -11.8 72 690 -17.2
North America 9 107 9 801 -7.1 101 119 -15.5
Argentina 388 326 19.0 3 651 -21.4
Brazil
2 886 2 462 17.2 30 971 -4.9
Chile 105 e 109 -3.5 1 165 2.8 Colombia 110 e 97 13.5 1 126 -15.5
Ecuador 50 e 50 0.5 477 -21.5
Paraguay 3 e 3 -4.4 22 -17.5
Peru 105 e 91 15.8 671 -45.4
Uruguay 5 e 5 -7.2 47 -24.6
Venezuela 2 e 0 315.8 29 -43.6
South America
3 654 3 143 16.3 38 158 -8.4
Egypt 994 574 73.0 8 229 13.4
Libya 73 63 16.2 495 -18.4
South Africa 292 e 297 -1.5 3 877 -37.0
Africa 1 359 934 45.5 12 600 -10.1
Iran 2 660 e 2 224 19.6 29 030 13.4
Qatar 85 186 -54.3 1 218 -52.4 Saudi Arabia 440 664 -33.8 7 775 -5.1
United Arab Emirates 280 297 -5.8 2 722 -18.2
Middle East 3 465 3 371 2.8 40 745 2.7 China 91 252 84 692 7.7 1 052 999 5.2 India 9 796 9 383 4.4 99 570 -10.6 Japan 7 526 7 785 -3.3 83 194 -16.2
South Korea 5 952 5 880 1.2 67 121 -6.0
Pakistan 380 e 261 45.6 3 743 13.3 Taiwan, China 1 700 e 1 693 0.4 20 570 -6.3 Thailand 410 e 357 14.8 4 420 4.1
Vietnam 1 600 e 1 876 19 500 11.6
Asia 118 616 111927 6.0 1 351 117 1.6
Australia 473 449 5.4 5 490 0.0 New Zealand 59 57 3.8 586 -12.2
Oceania 533 506 5.2 6 076 -1.4
Total 64 countries (1) 160 858 151969 5.8 1 829 140 -0.9 (1) - HADEED only. (2) - the 64 countries included in this table accounted for approximately 99% of total world crude steel production in 2019. e - estimated www.skillings.net | 47
















 MARIE GABRIELLE LAGUNA
MARIE GABRIELLE LAGUNA





 JOHN EDWARD
JOHN EDWARD













































